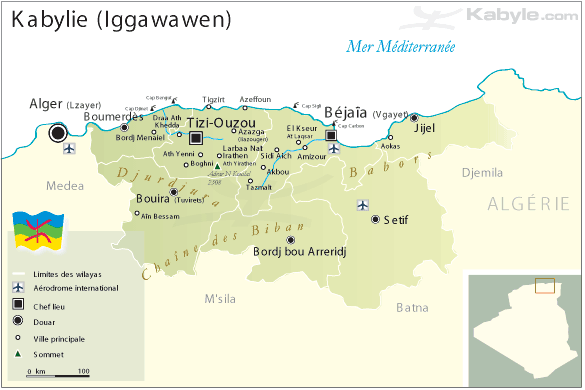
Outrage after police slaying of Atlanta forest defender
Protests and vigils have been held across the US following the police slaying of environmental activist Manuel Teran, 26, also known as Tortuguita, in Georgia’s Dekalb County. A protest over the killing turned violent in downtown Atlanta, with a police car burned, windows smashed, and several arrested. Tortuguita was shot in a police raid on an encampment in the Weelaunee Forest, a threatened woodland within the South River Forest conservation area. The Atlanta Police Foundation seeks to clear a large area of the forest in order to build a $90 million Public Safety Training Center, referred to as “Cop City” by local residents. Authorities say a Georgia state trooper was also shot and injured in the raid. (Image: It’s Going Down)