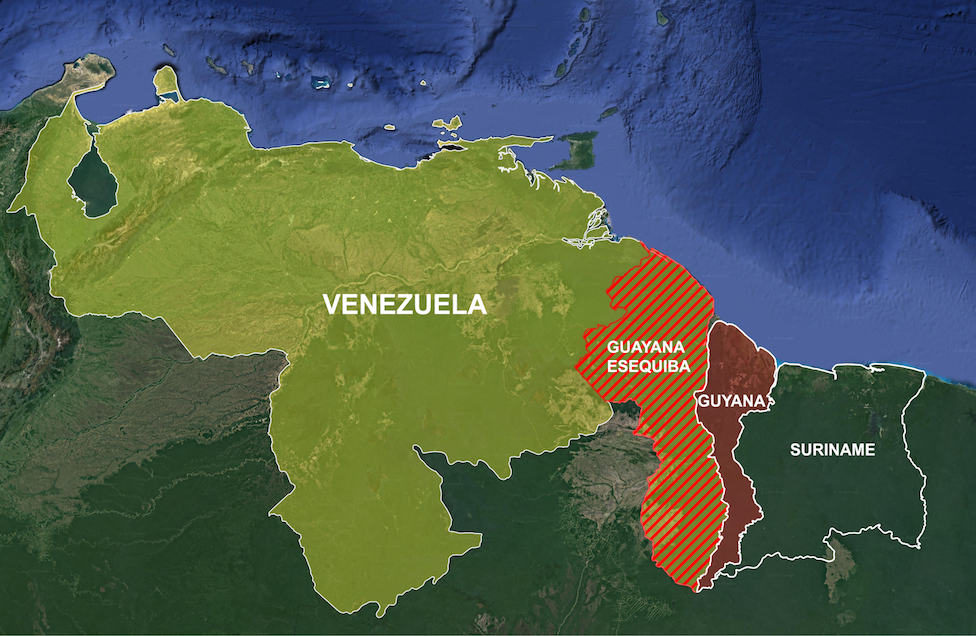
Haiti gangs profit from mission delay
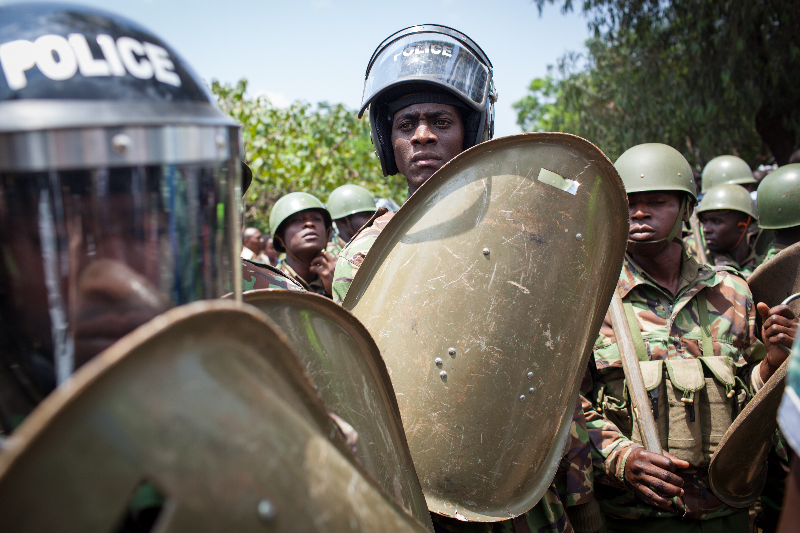
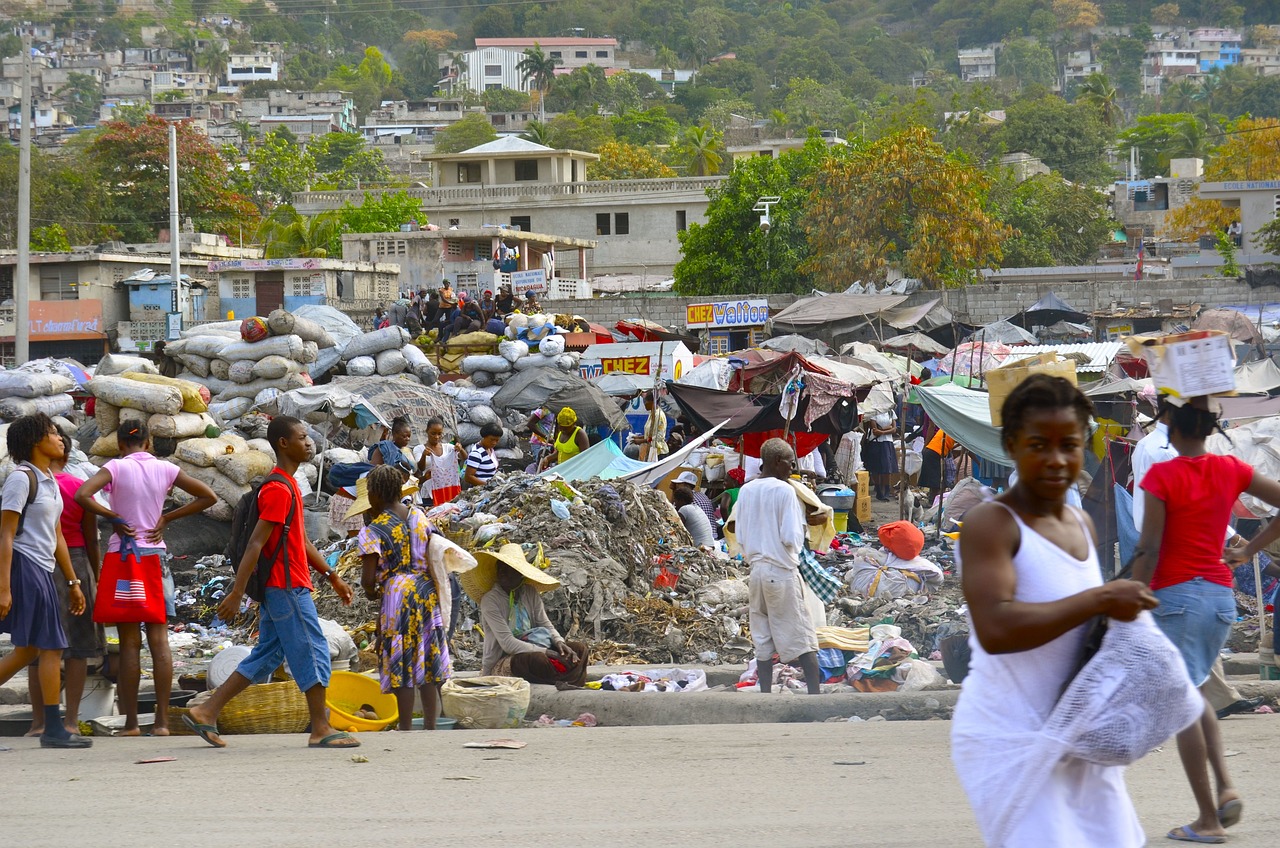
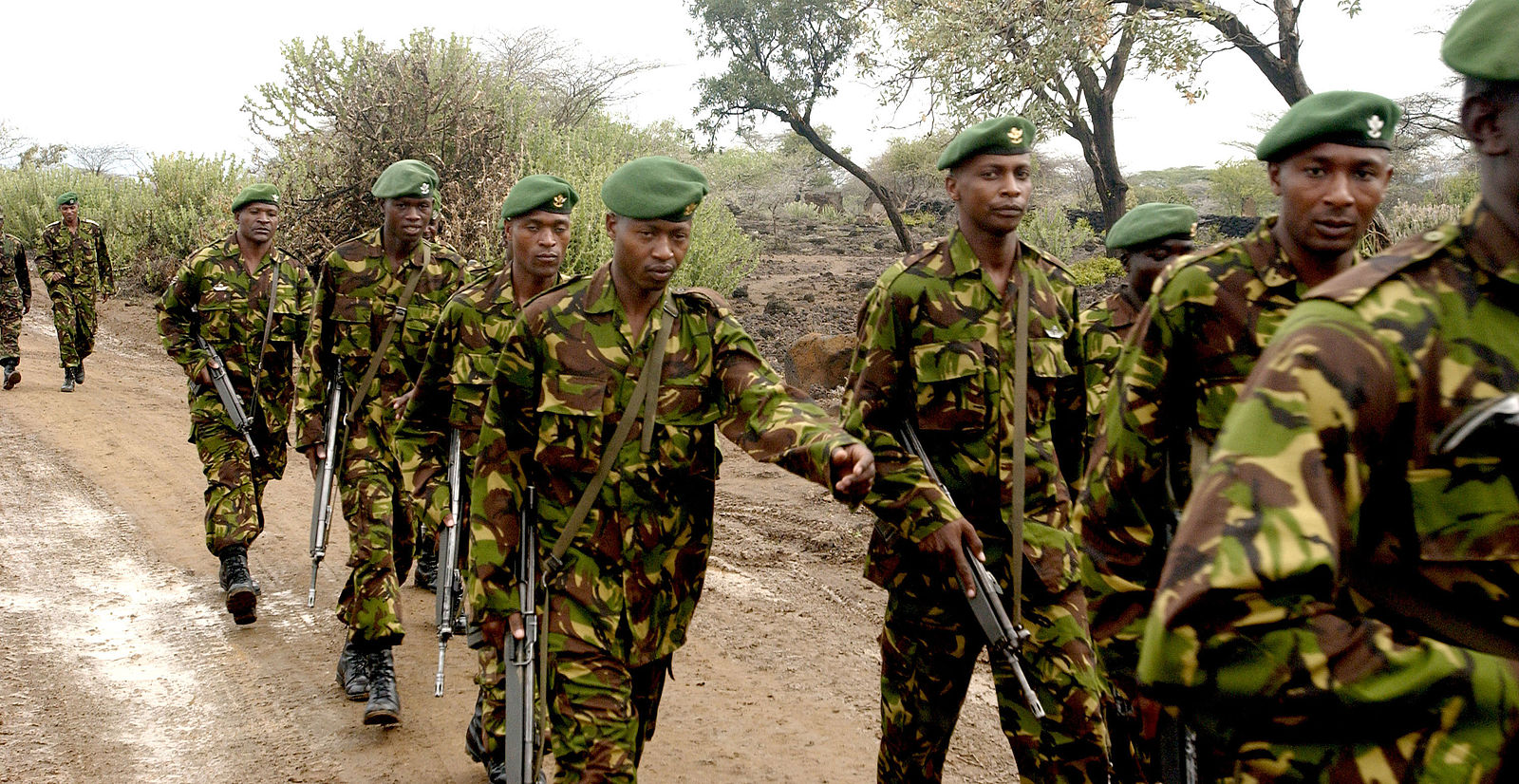
The continually delayed deployment of a Kenya-led Multinational Security Support (MSS) mission has raised concerns over how prepared the UN-approved and US-bankrolled force will be to face the security crisis in Haiti. The violent gangs that now control most of Port-au-Prince have posted direct threats to the MSS force and paraded their heavy weaponry on social media. Amid reports of a large inventory of Colombian weapons being trafficked to Haitian gangs, some experts worry that the firepower of the gangs has been underestimated. One analysis warns that the gangs are exploiting the delays to “fortify what could be a fierce response.” (Photo: Haiti Liberte)