Podcast: Tolstoy would shit
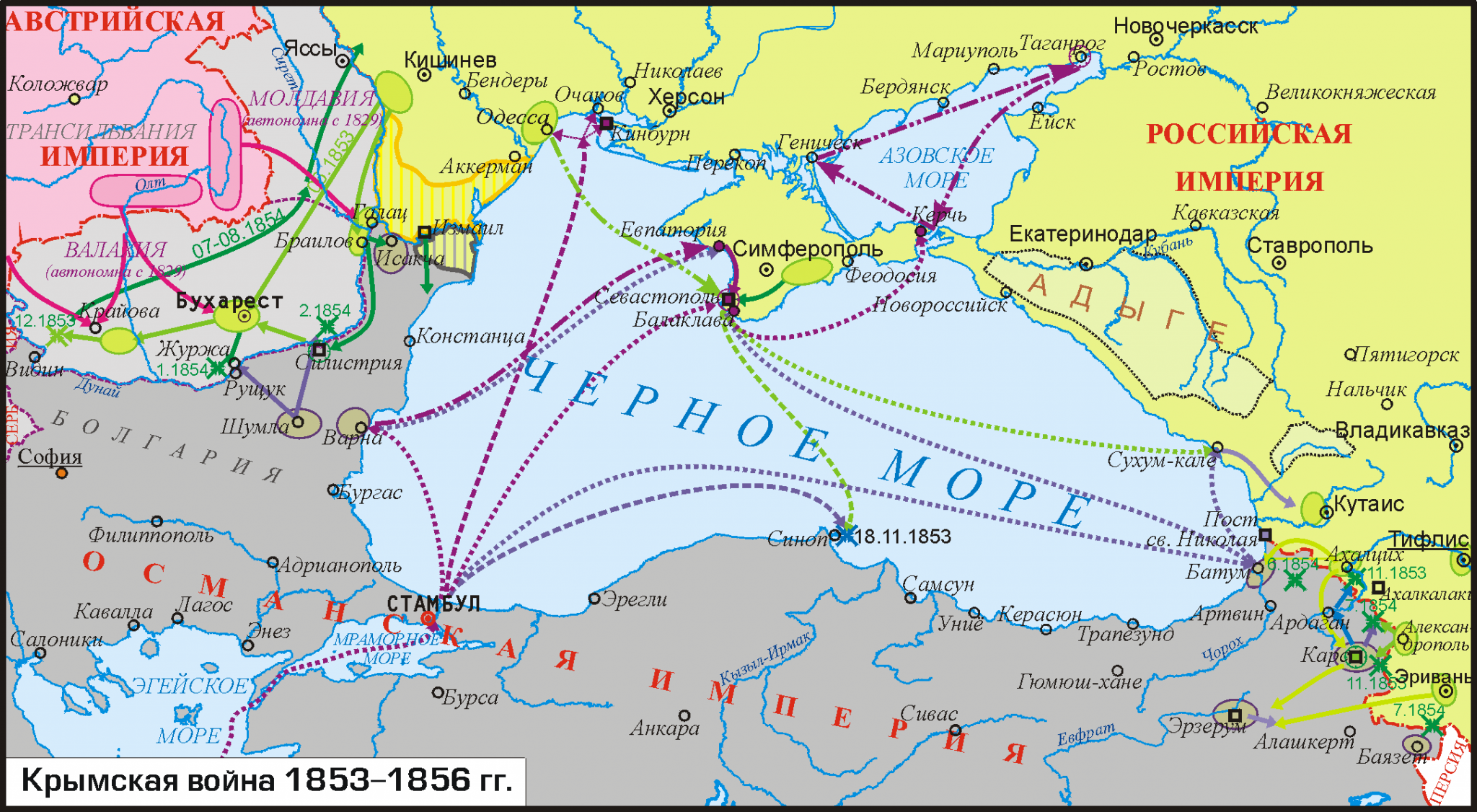
In Episode 132 of the CounterVortex podcast, Bill Weinberg notes that deputy Duma speaker Pyotr Tolstoy, one of the most bellicose supporters of Putin’s Ukraine war, is a direct descendent of Leo Tolstoy—and recently invoked his great-great-grandfather’s “slaughter” of British and French troops during the Crimean War as a warning to the West. This is, of course, an utterly perverse irony given that the literary giant’s anarcho-pacifist beliefs were antithetical to everything that his descendant Pyotr stands for. Indeed, it was Leo Tolstoy’s experiences in the Crimean War that turned him into a committed pacifist. His final novel, Hadji Murat, vivdly depicts the brutality of Russia’s counterinsurgency campaign in Chechnya in the 1850s—a history that repeated itself in Chechnya in the 1990s. This is bitterly recalledby the Chechen volunteers now fighting for Ukraine, where this history is repeating itself yet again. Listen on SoundCloud or via Patreon. (Image adopted from Europeana Foundation)