Morocco: Melilla massacre survivors get prison
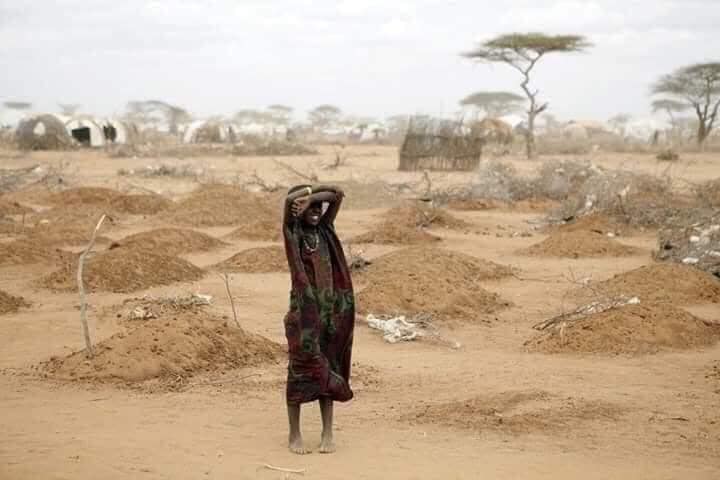
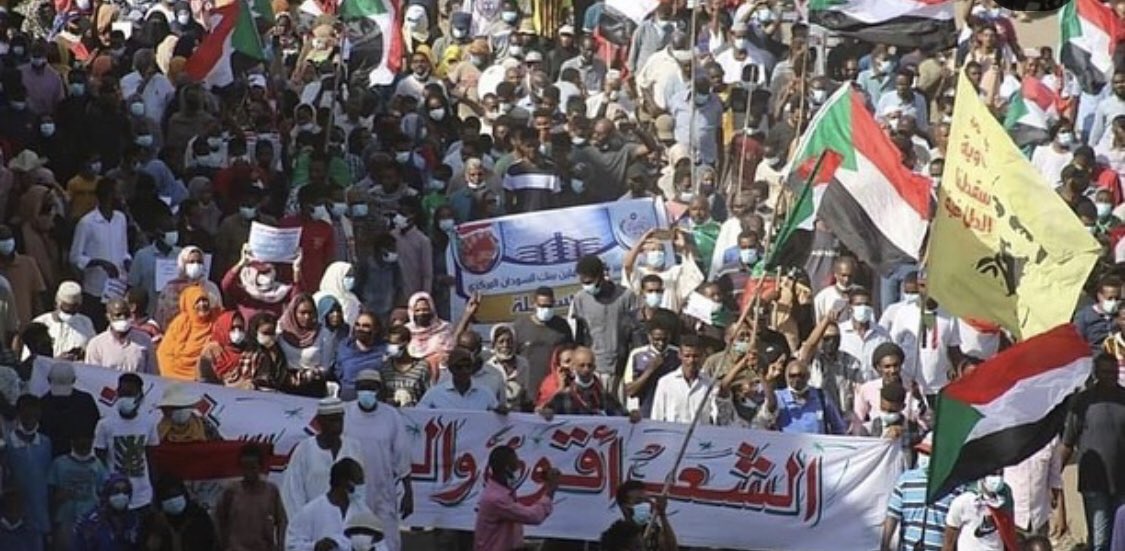
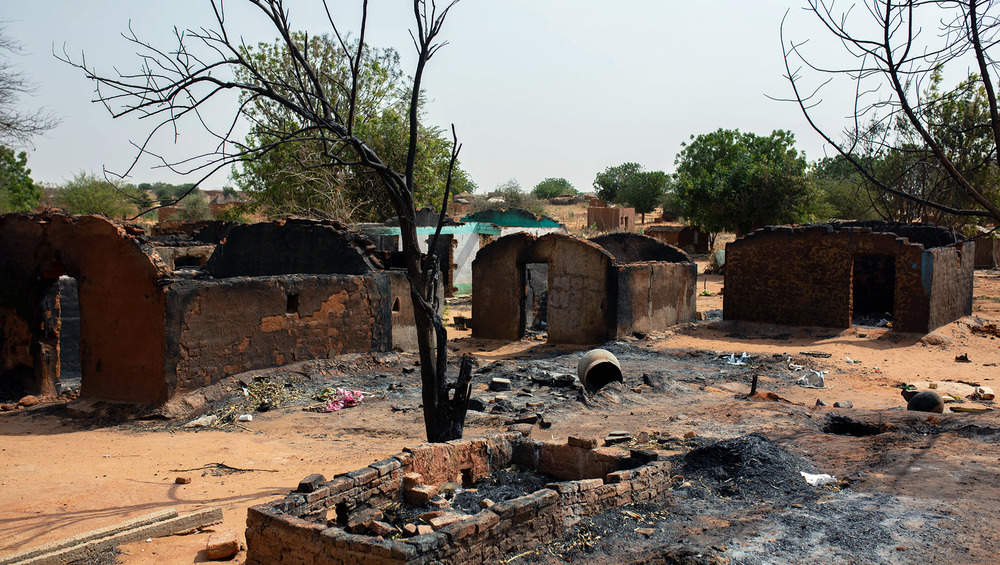
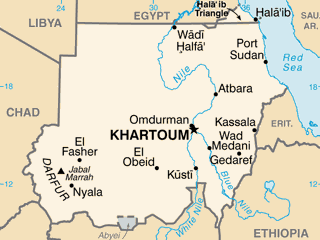
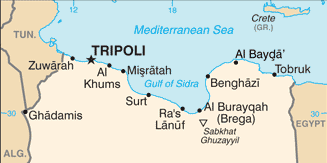
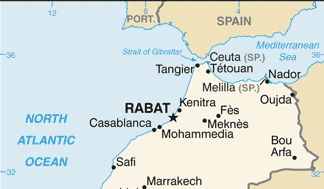
A court in Nador, Morocco, sentenced 33 migrants, mostly from Sudan and South Sudan, to 11 months behind bars for “illegal entry” into the country and “disobedience.” The 33 are among the hundreds who last month attempted to enter Spain’s North African enclave of Melilla, sparking a violent response from authorities. Some 2,000 migrants stormed the heavily fortified border between the Moroccan region of Nador and the Spanish enclave, with many trying to scale the border wall. They were repelled by Moroccan and Spanish security forces, with up to 27 killed. The African Union is calling for an investigation into the repression. (Map: PCL Map Collection)