Russian indigenous leaders protest Putin’s war
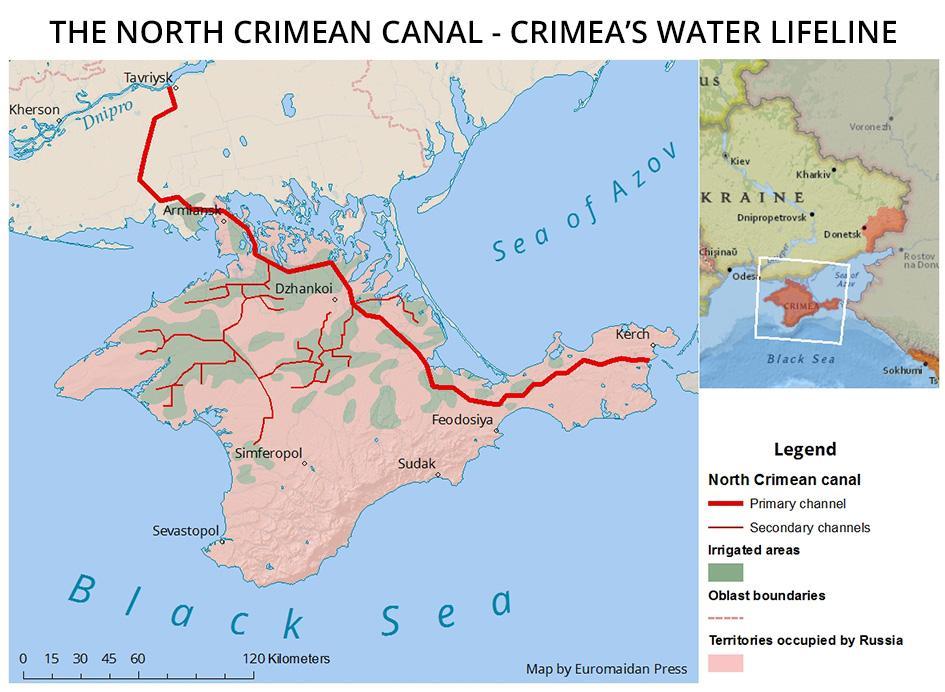
Exiled leaders of Russia’s Itelmen, Kamchadal, Udege, Shor, Saami and Selkup indigenous peoples issued a statement declaring that they are “outraged by the war President Putin has unleashed against Ukraine. At the moment, the entire population of Ukraine is in grave danger. Old people, women and children are dying. Cities and towns of an independent country are being destroyed because their inhabitants did not want to obey the will of a dictator and a tyrant.” The statement adds: “As representatives of Indigenous peoples, we express solidarity with the people of Ukraine in their struggle for freedom and are extremely concerned about ensuring the rights of Indigenous peoples during the war on Ukrainian territory, including the Crimean Peninsula that remains illegally occupied by Russia.” (Photo of Itelmen people in the Kamchatka Peninsula via Wikipedia)