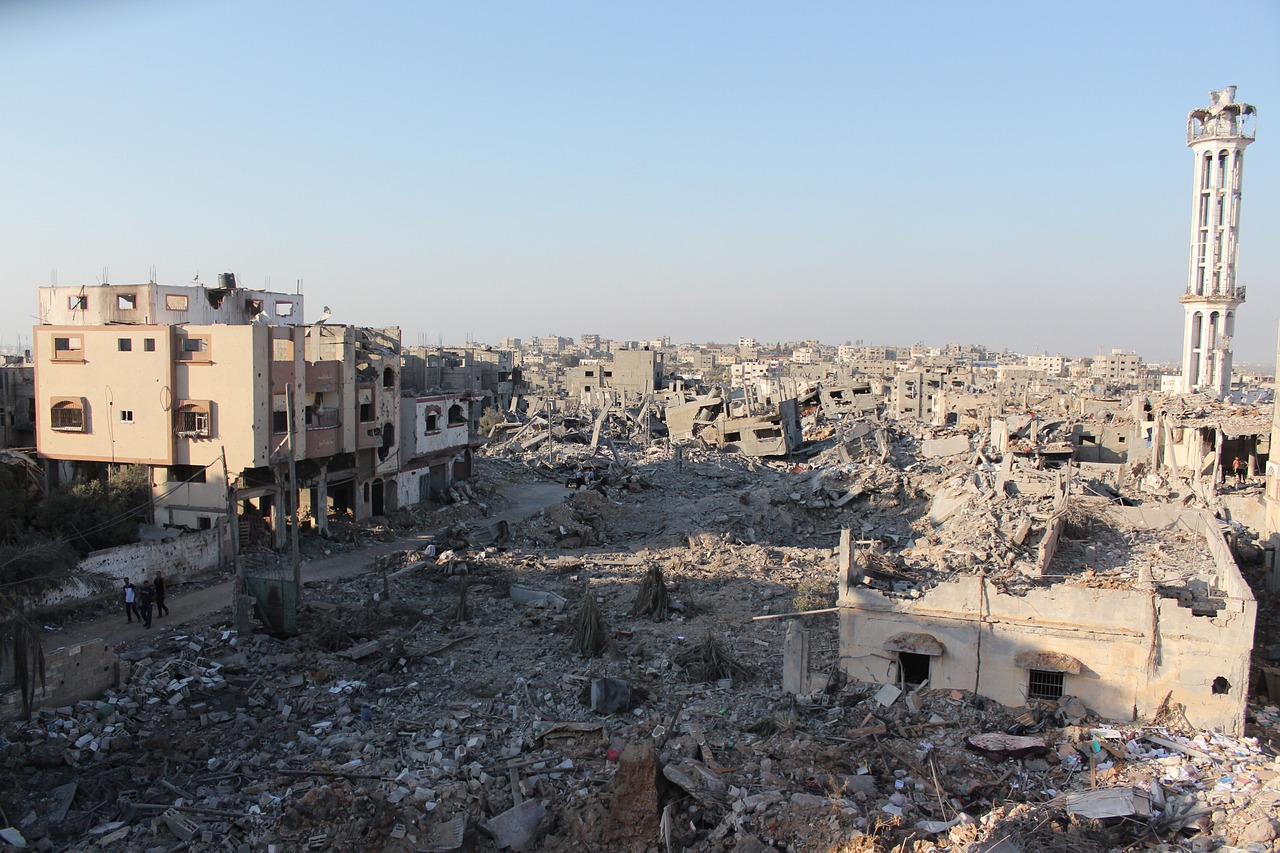
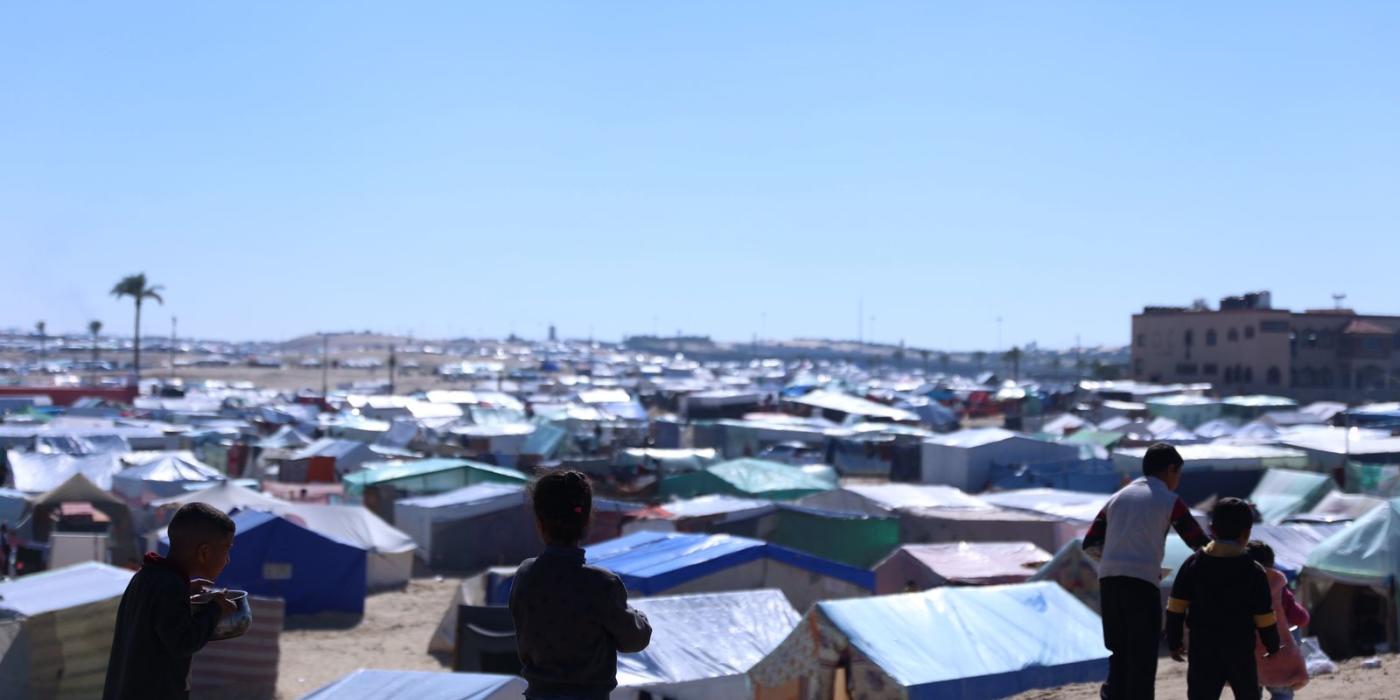
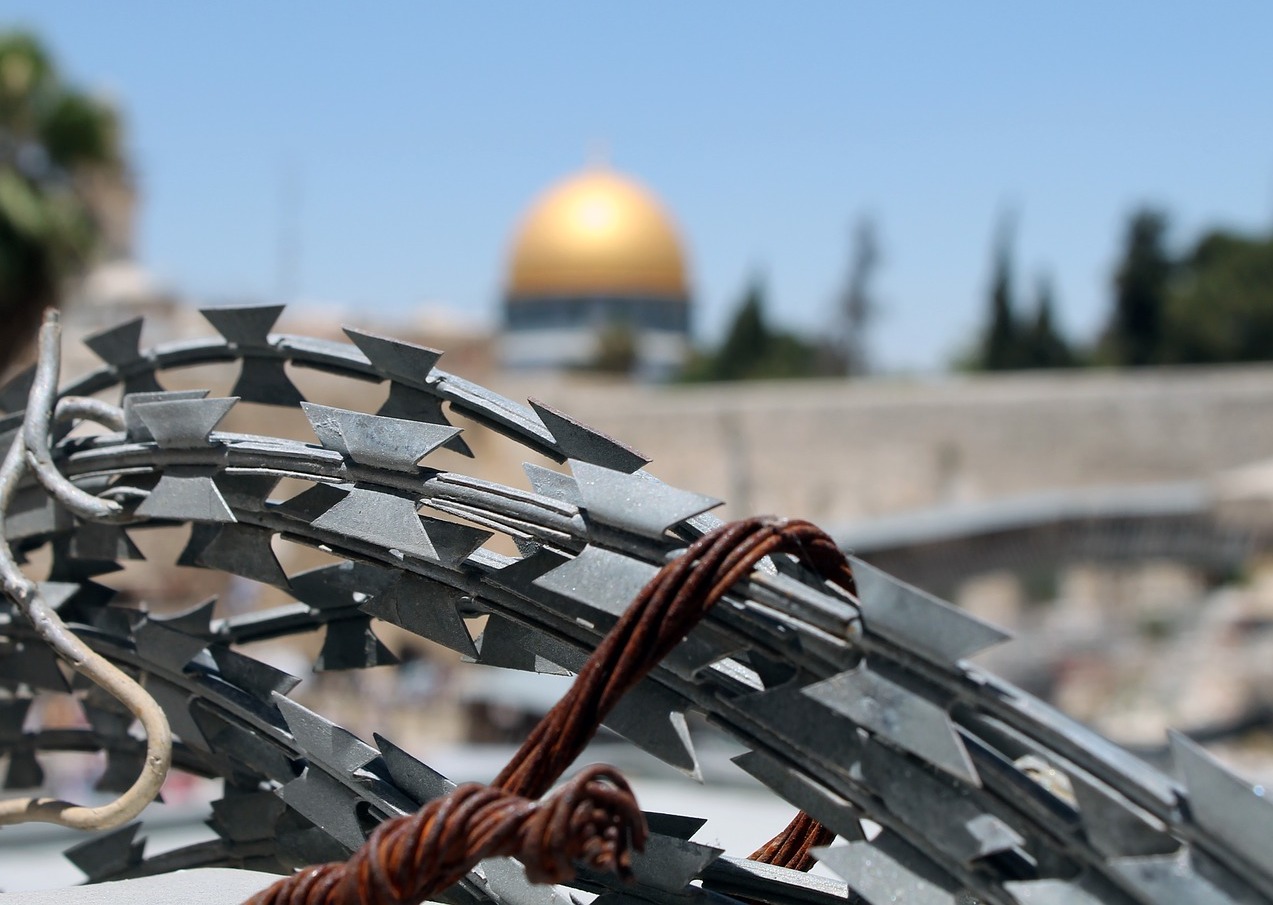
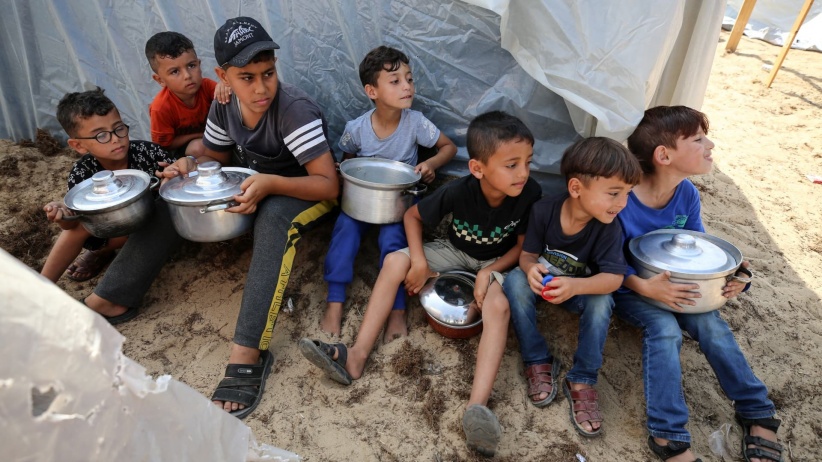
Pressure mounts for arms embargo on Israel
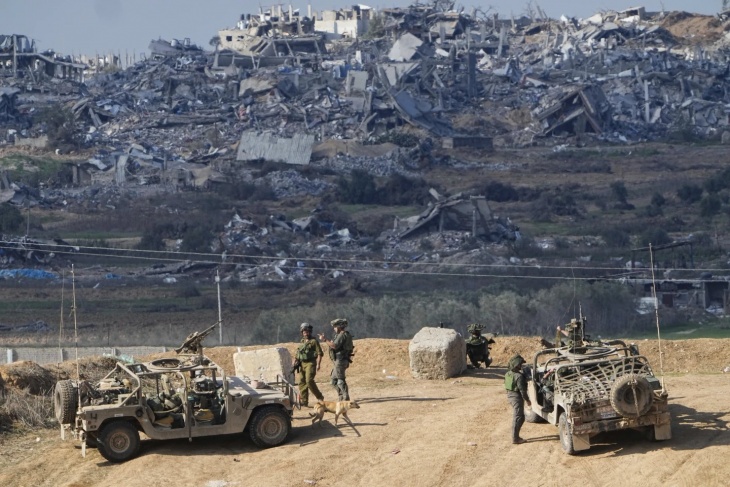
The UN Human Rights Council adopted a resolution, A/HRC/55/L.30, reiterating the Security Council’s call for an immediate ceasefire in Gaza—and further calling for an embargo and prevention of the supply of weapons to Israel by UN Member States. Simultaneously, 40 Democratic members of the US House of Representatives signed a letter to President Joe Biden urging him to cease arms transfers to Israel in the wake of the air-strike that killed seven humanitarian aid workers in Gaza. Meanwhile in Germany, human rights lawyers filed a motion in the Berlin Administrative Court to halt the Federal Republic’s arms exports to Israel. The lawyers claim that the German government has committed the crime of aiding and abetting in the genocide of the Palestinian people living in Gaza by continuing to supply Israel with arms. (Photo: hosnysalah/Pixabay via Jurist)