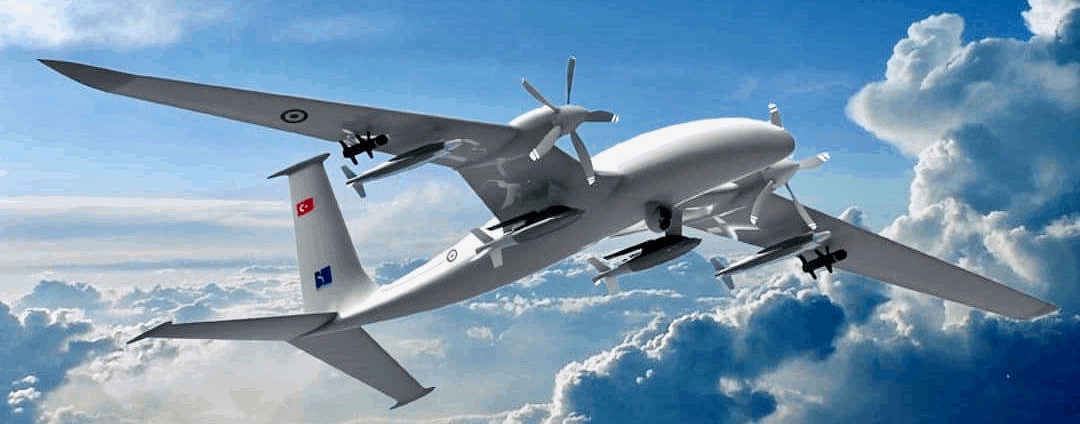
Turkish drones decisive in regional wars
The Turkish military is unveiling a new upgraded “unmanned combat aerial vehicle,” the Bayraktar Akıncı, developed by private drone manufacturer Baykar Defense, which is owned by President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan’s son-in-law Selçuk Bayraktar. The Akıncı is a more advanced version of Turkey’s iconic Bayraktar TB2, able to fly higher and carry more missiles. The TB2 has been used by Ankara against Kurdish guerillas in northern Iraq, and against Syrian regime forces. Turkey has also provided the TB2 to various foreign militaries; it is held to have been decisive in Azerbaijan’s victory over Armenian forces in last year’s Nagorno-Karabakh war, as well as the Libyan government’s victory over the warlord Khalifa Haftar. Ukraine, having already tested an initial dispatchment of the drone, is now ordering 24 more for use in its war against Russian-backed separatists. (Photo: Wikipedia)