Mining disaster wipes out community in Ghana
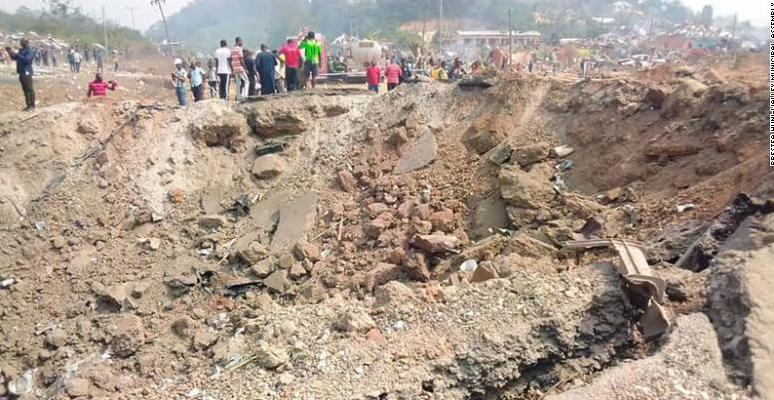
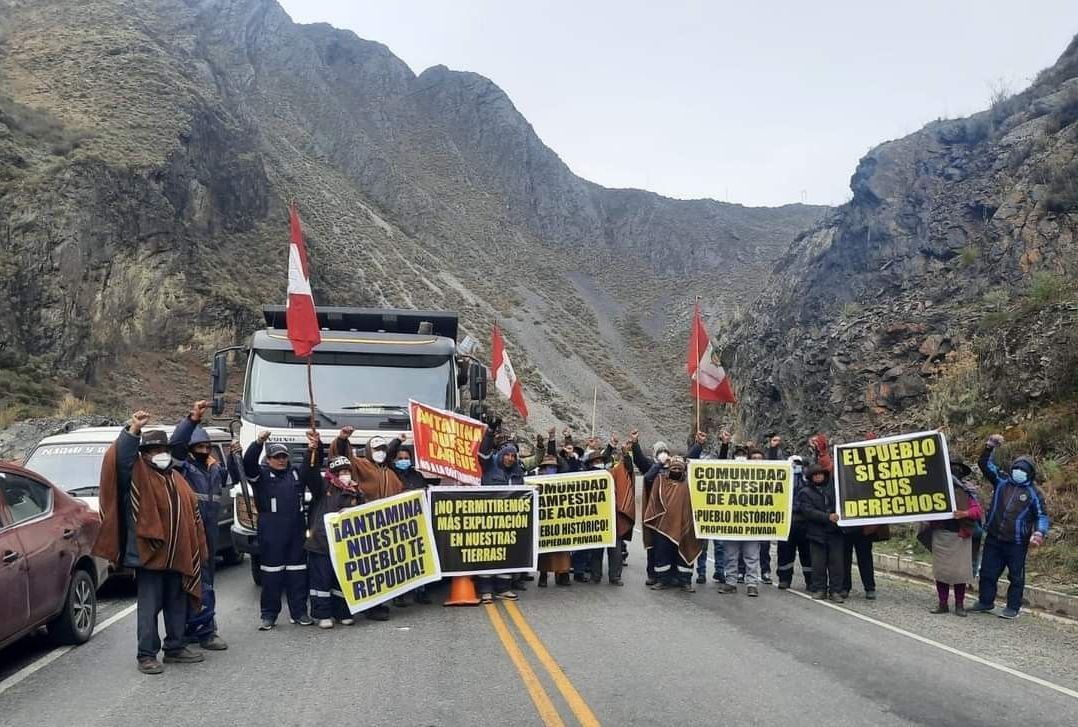
A rural community in Ghana’s Western Region was virtually flattened when a truck carrying explosives to a gold mine collided with a motorcycle, setting off a massive blast. Some 40 have been hospitalized, and the official death toll of 17 is expected to rise. The truck, owned by a local mining services company called Maxam, was en route to the Chirano gold mine, operated by Toronto-based Kinross Gold. The explosion left a huge crater and reduced dozens of buildings to dust-covered piles of wood and metal in the community of Apiate, near the city of Bogoso, some 300 kilometers west of the capital Accra. The chief executive of Prestea Huni-Valley municipality told local media “the whole community is gone” after the blast. (Photo: Prestea Huni-Valley Municipal Assembly via Mining.com)