Trump tariffs ‘inexplicably cruel’ for Africa
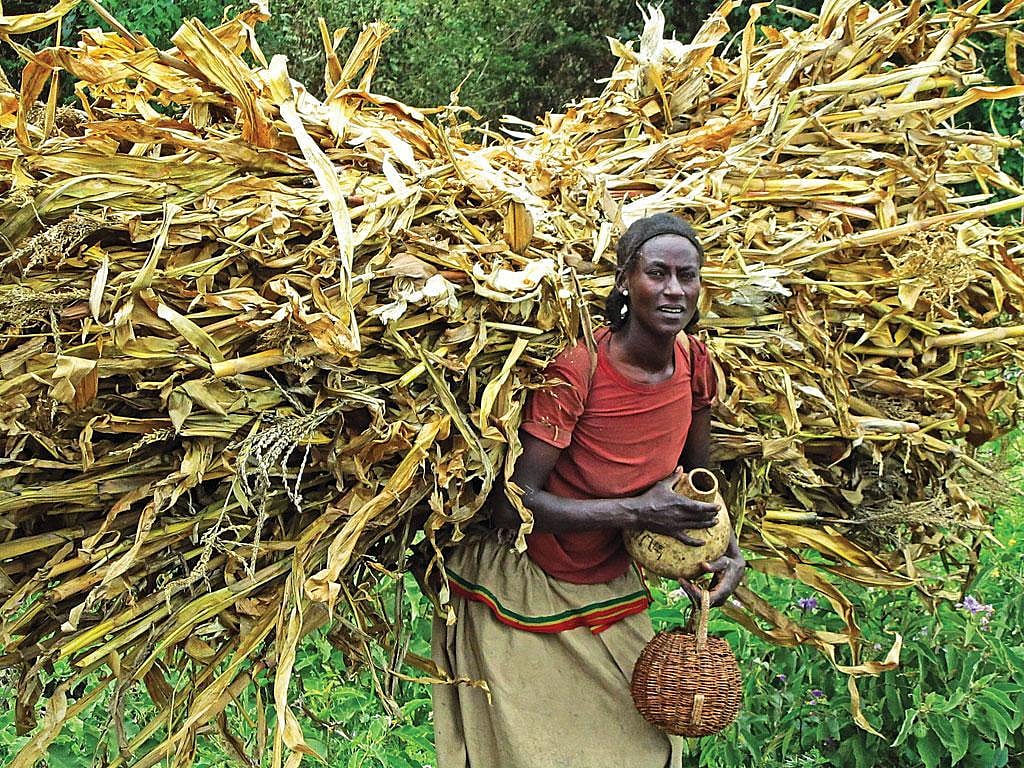
Some of the world’s poorest countries, including nations grappling with protracted humanitarian crises, are among those most affected by President Donald Trump’s new trade tariffs regime, which has compounded pre-existing economic strains and debt woes. Among the worst effects will likely be felt in Africa, where Trump’s decision has created an “inexplicably cruel situation,” according to the Center for Global Development (CGD). “It is hard to fathom that the administration set out to destabilize poor African countries and unclear what they hope to gain,” wrote CGD researchers. The tariffs have effectively tanked the African Growth & Opportunity Act (AGOA), which allowed duty-free imports to the US for 32 countries and was credited with helping economic growth. Amid existential financial worries in the international aid sector—triggered by Trump’s closure of USAID—economists have also raised the possibility of a global trade war, with far-reaching ramifications for inflation and the cost of living worldwide. (Photo: Down To Earth)