UN human rights office: Taliban not ‘reformed’
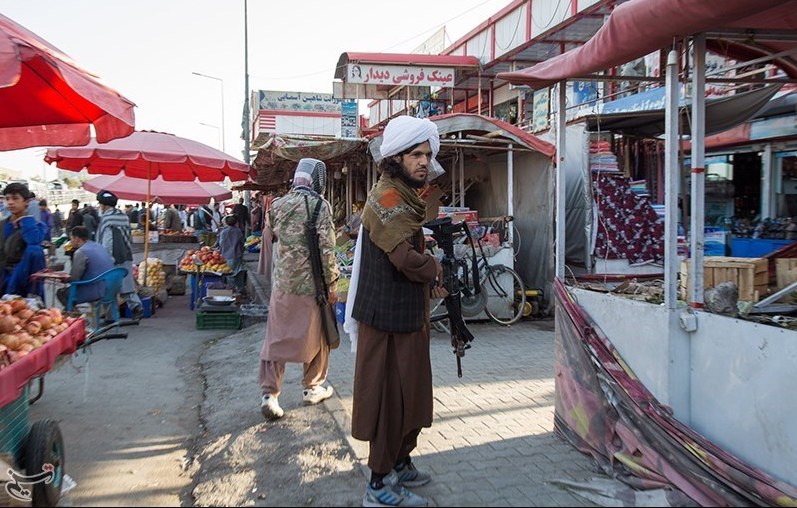
The United Nations Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) released a statement condemning the idea that the Taliban are “reformed” since the last time they were in power in Afghanistan. The statement, written by multiple human rights experts, drew attention to the gap between the promises made by the Taliban upon its return to power in August 2021 and the reality of “gender apartheid” in Afghanistan. (Photo: Milad Hamadi/Tasnim News Agency via Wikimedia Commons)