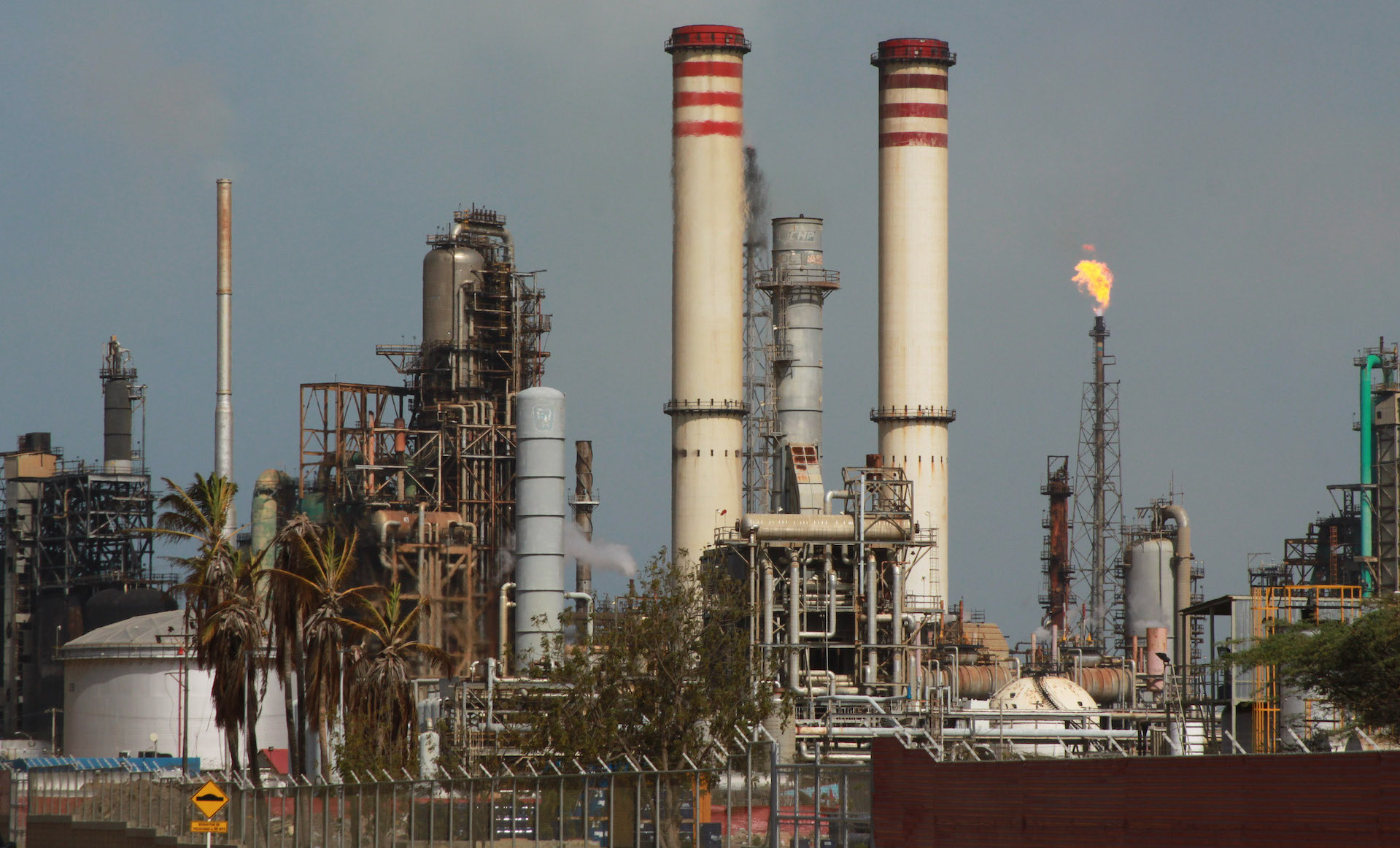
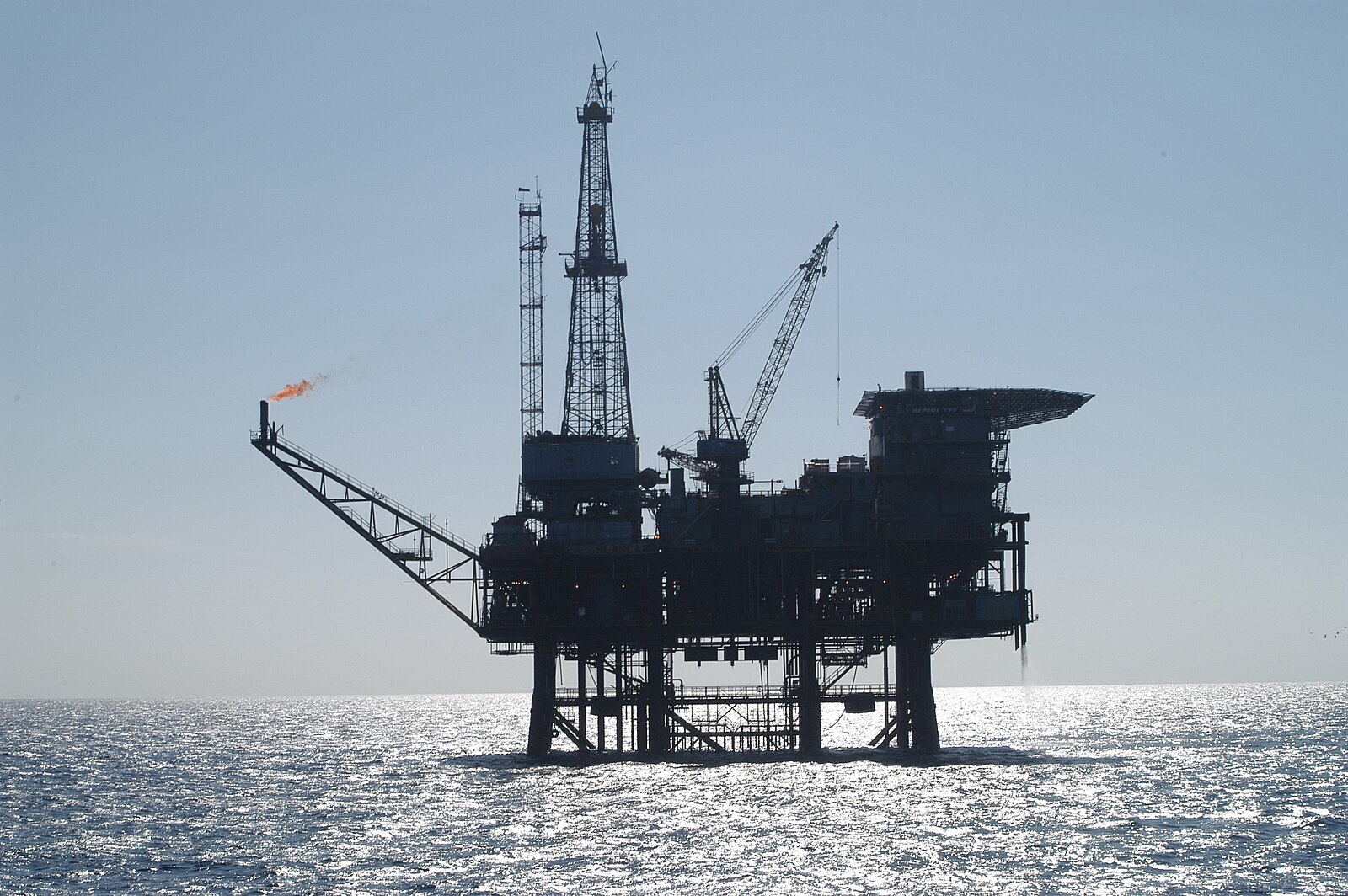
Venezuela: Trump restores sanctions on Chevron operations
President Donald Trump announced that the US government is revoking a special permit granted to energy giant Chevron to pump and export Venezuelan oil. The move, which reverses a 2022 decision by Biden to allow the company to bring Venezuelan oil to US markets by exempting it from economic sanctions, removes one of the South American country’s few economic lifelines at a time of deepening crisis. In his post on TruthSocial, Trump claimed that the Venezuelan government had failed to keep up its side of the original bargain to meet “electoral conditions.” He also charged that the “regime has not been transporting the violent criminals they sent into our Country…back to Venezuela at the rapid pace that they had agreed to.” (Photo: Luis Ovalles via Dialogo Americas)