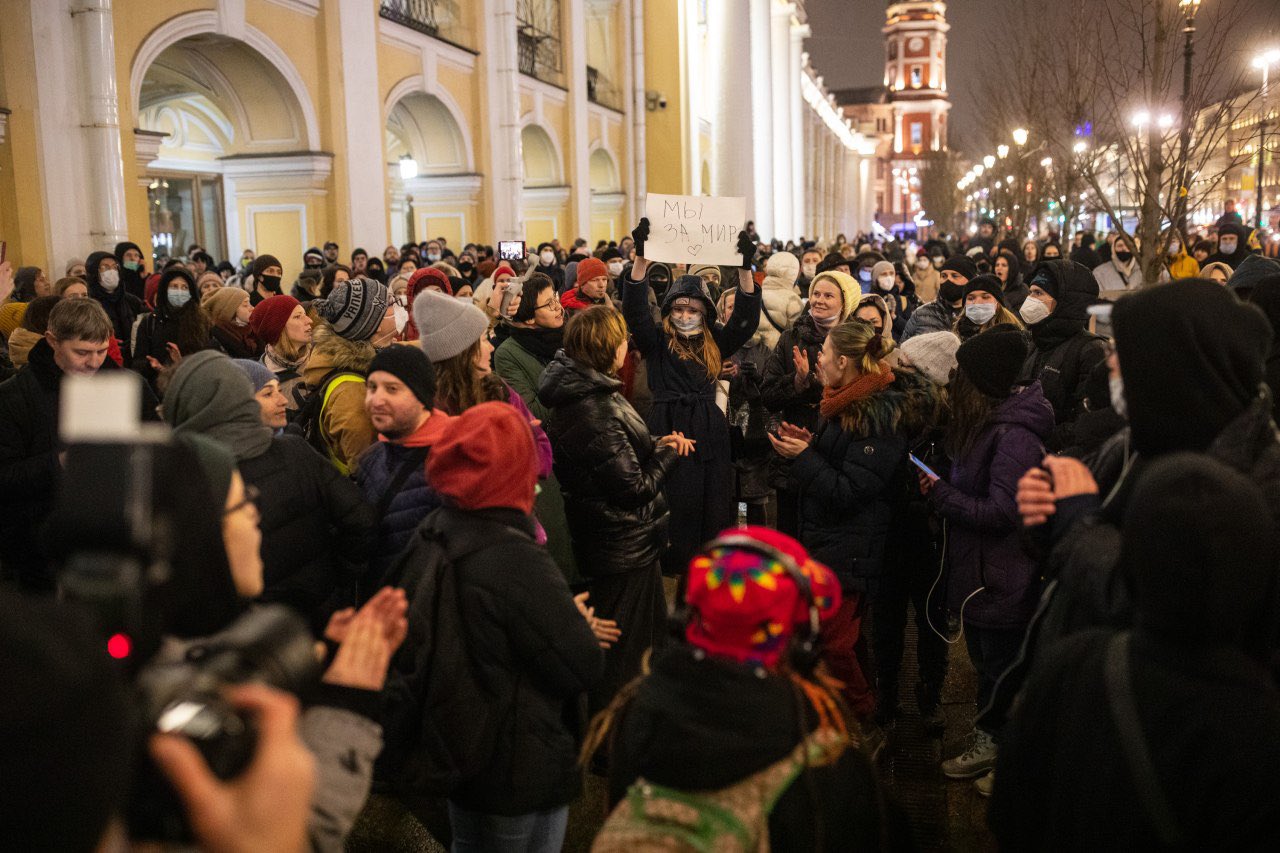UN Human Rights Council to investigate Russian violations in Ukraine
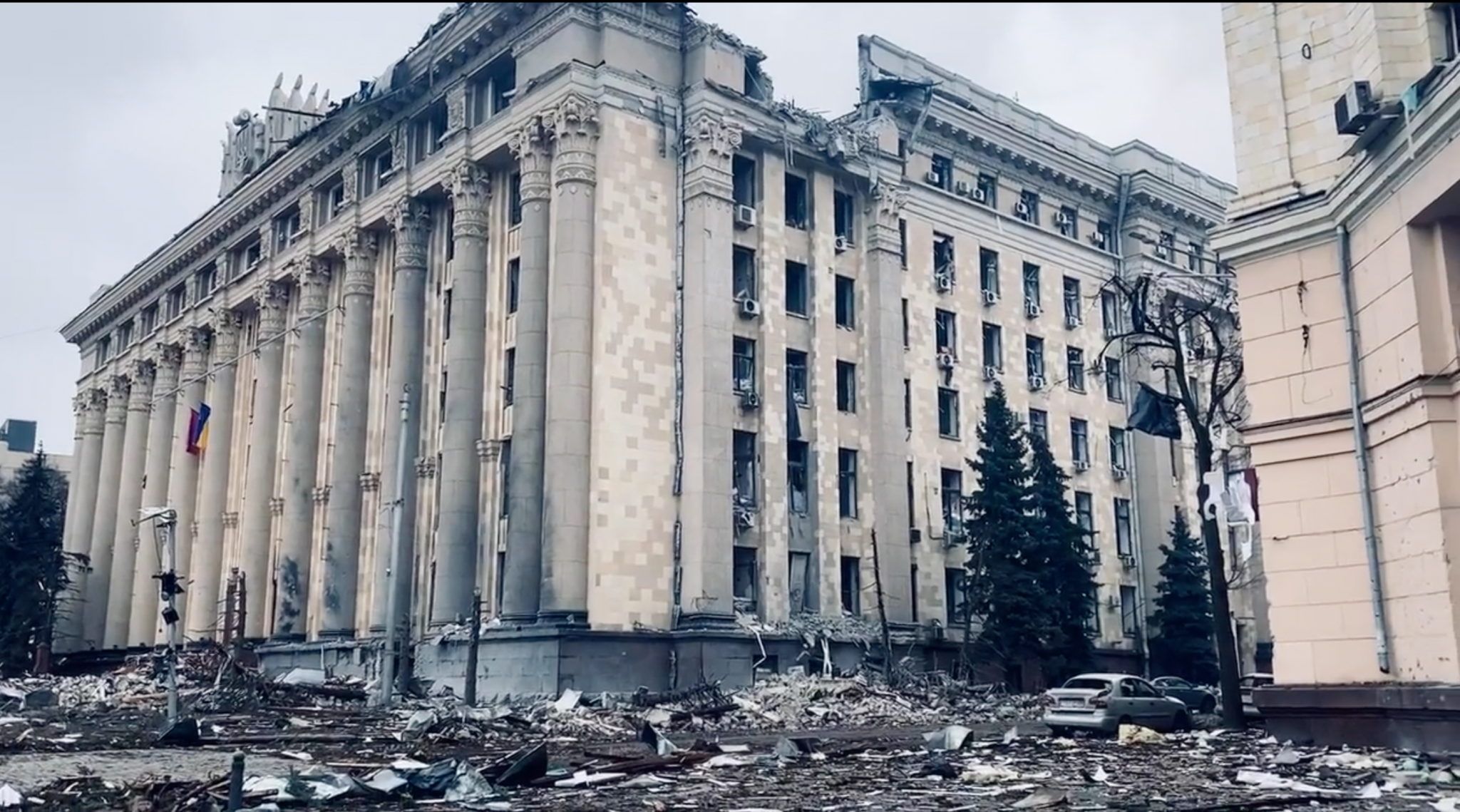
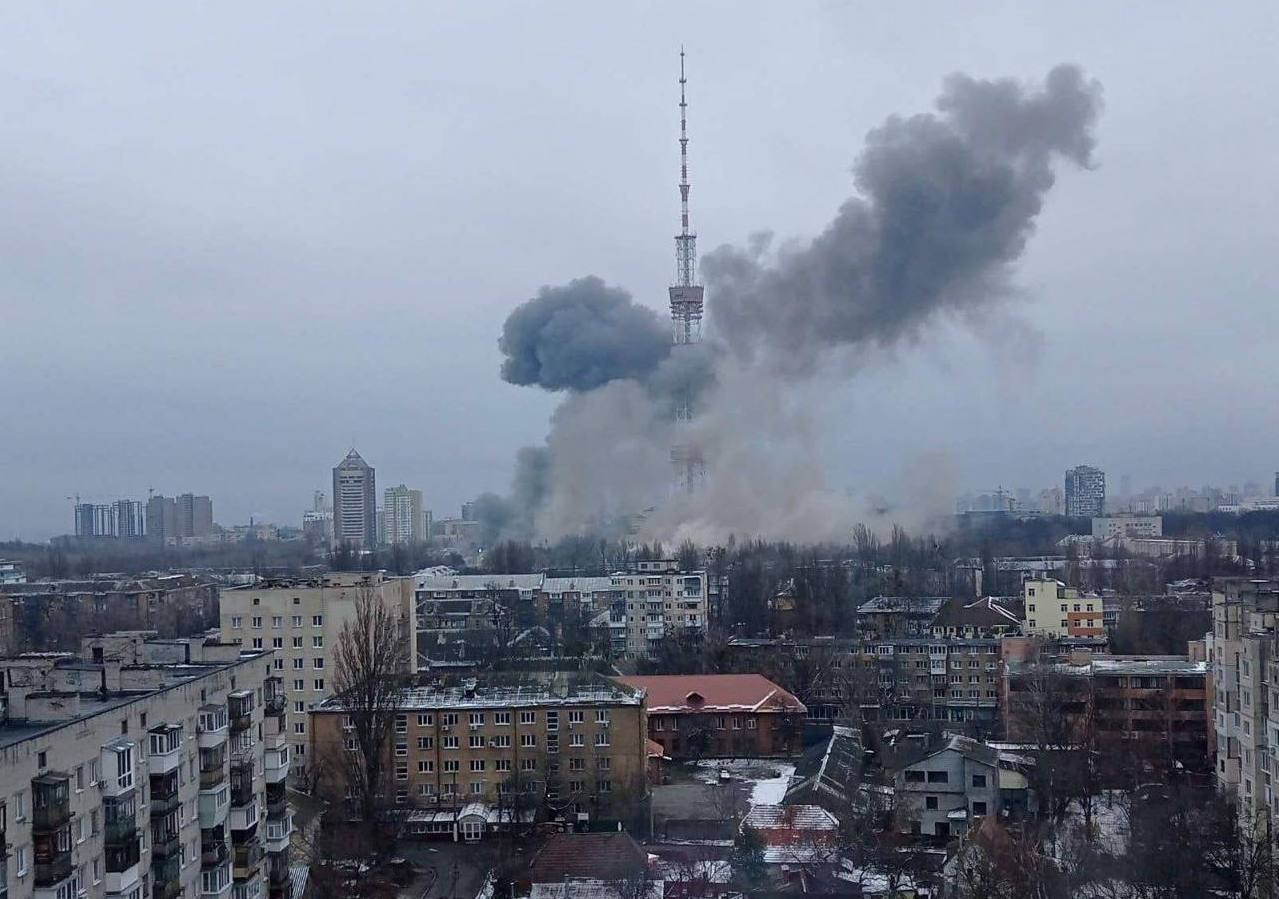
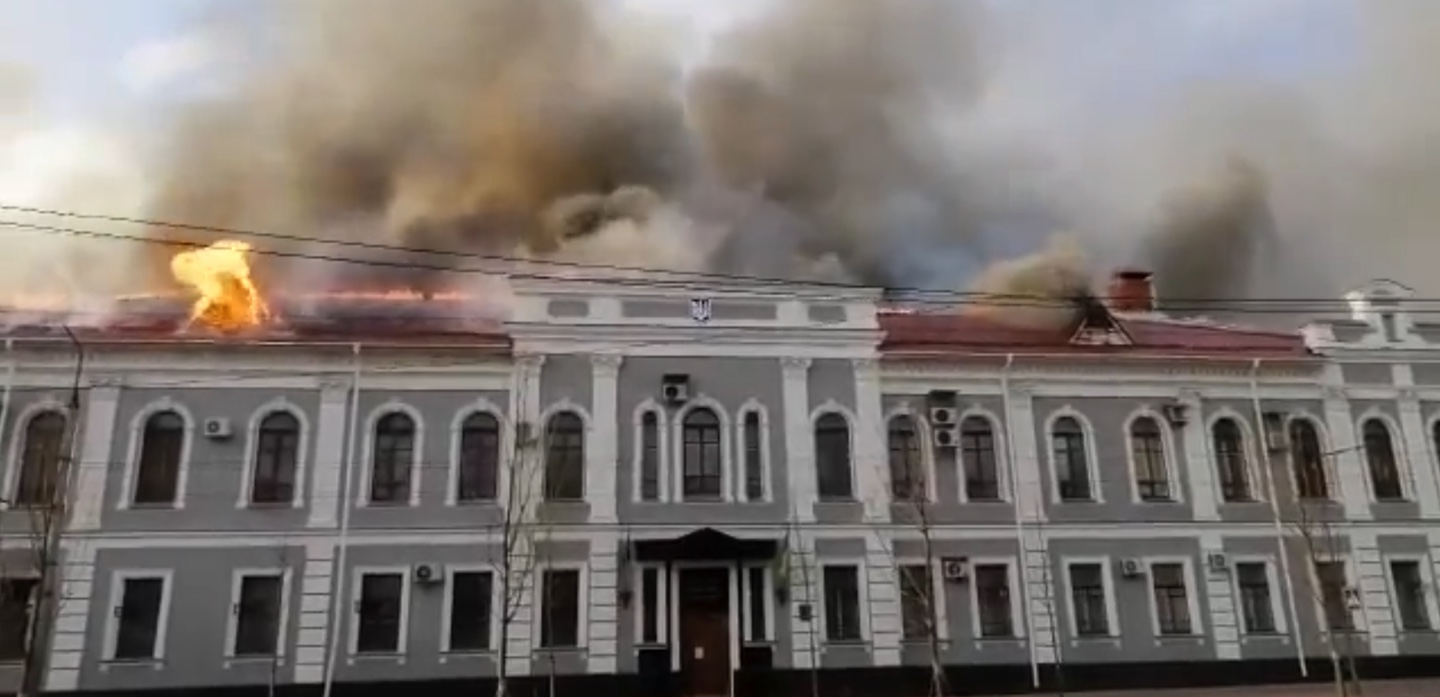
The UN Human Rights Council (HRC) adopted a resolution to establish an Independent International Commission of Inquiry to investigate charges of gross violations by Russian forces in Ukraine. After holding a moment of silence for Ukrainian victims, HRC members passed the resolution overwhelmingly, in a 32–2 vote. The only two countries voting against were Russia and Eritrea. Significantly, China and Cuba abstained. (Photo of Kharkiv’s Freedom Square via Twitter)