Podcast: climate change and the global struggle III
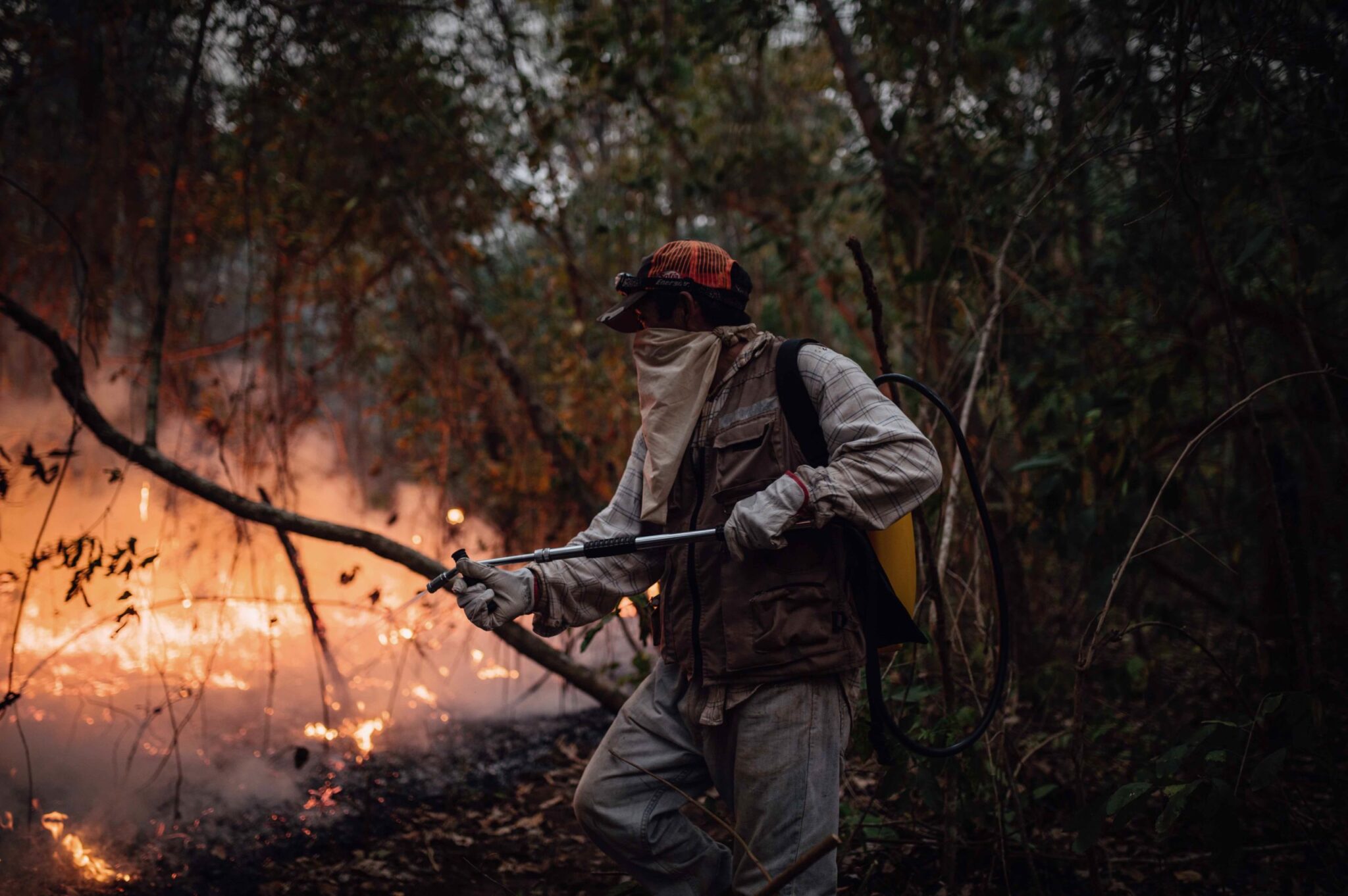
In Episode 151 of the CounterVortex podcast, Bill Weinberg notes a tellingly ironic juxtaposition of simultaneous news stories: the COP27 global climate summit in Egypt and the World Cup games in Qatar—where mega-scale stadium air-conditioning betrays the fundamental unseriousness of our civilization in addressing the impending climate apocalypse. The COP27 agreement for a “loss and damage” fund stopped short of demands for climate reparations—a critical question for island nations that stand to disappear beneath the waves, flood-devastated Pakistan, and indigenous peoples of the fire-ravaged Bolivian Amazon. Petro powers like Russia and Saudi Arabia formed a bloc to bar any progress on limiting further expansion of oil and gas exploitation, while the Ukrainian delegation called for a boycott of Moscow’s hydrocarbons, and pointed to the massive ecological toll of Russia’s war of aggression. Meanwhile, the world population reached 8 billion, providing an excuse for groups like PopulationMatters to proffer the Malthusian fallacy even as the rate of population growth is actually slowing. Worldwide indigenous and peasant resistance to hydrocarbon exploitation points to a revolutionary answer to the crisis. Listen on SoundCloud or via Patreon. (Image: Bolivian campesino volunteer fire-fighter. Credit: Claudia Belaunde via Mongabay)