Yemen: Houthis obstruct aid amid deepening disaster
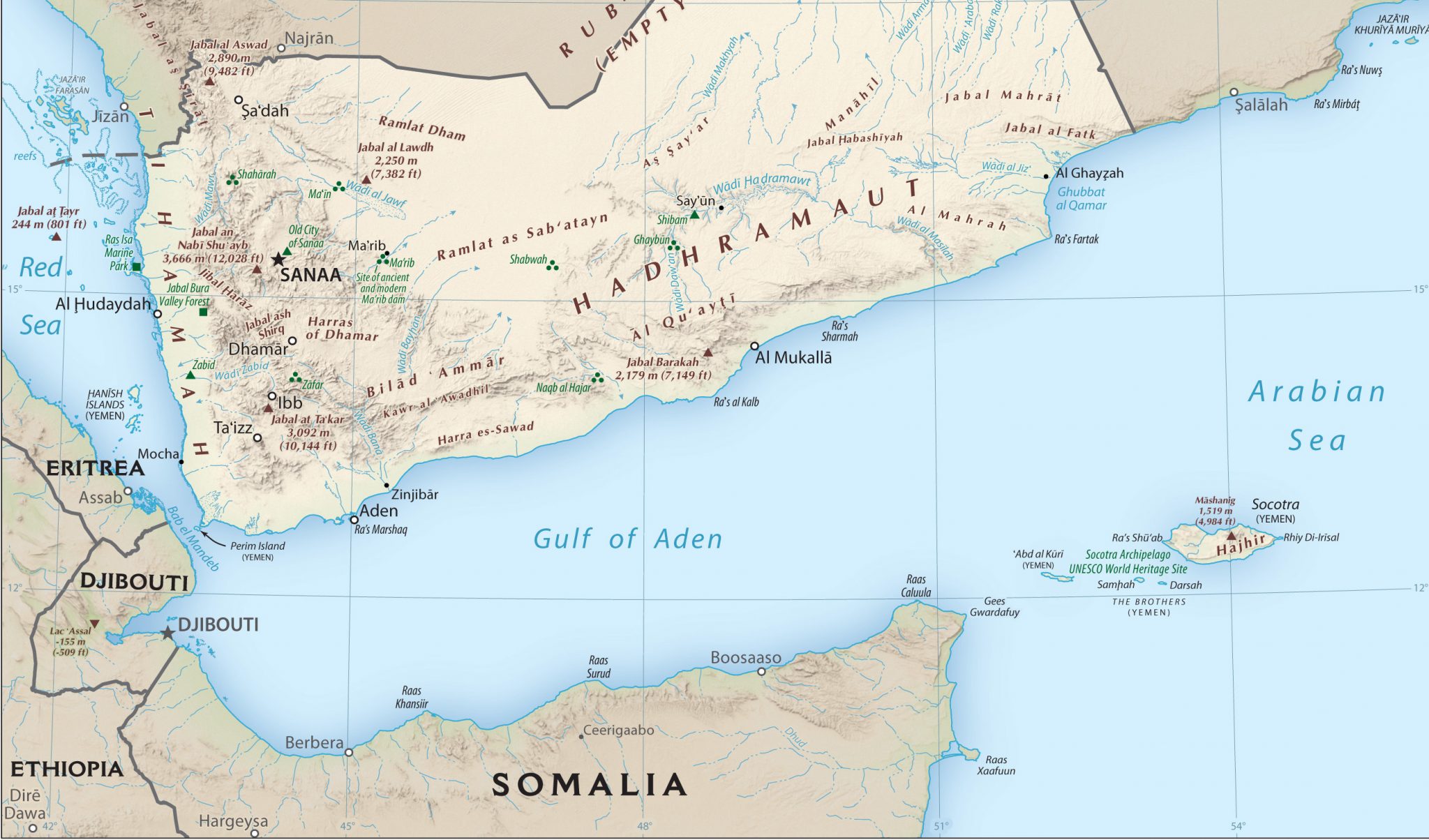
Flooding in Yemen’s coastal Hodeidah province has killed at least 30 people, while floods in the inland district of Taizz killed 15. The World Health Organization reports severe damage to homes and infrastructure, with contaminated water worsening the cholera outbreak in the country. Meanwhile, Human Rights Watch said in a new report that authorities across Yemen have “obstructed aid” to stricken areas, and “failed to take adequate preventative measures to mitigate the spread of cholera.” The report especially criticizes such obstruction by the Houthi forces, who have for years maintained a siege of Taizz. (Map via PCL)