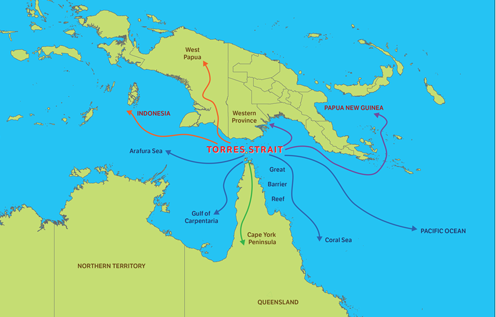
Strategic strait at issue in Australia-China rift
Amid trade wars, diplomatic tiffs and propaganda sniping, the ugliness between China and Australia seems set to escalate as Beijing enters an agreement with Papua New Guinea to establish an industrial foothold within the narrow Torres Strait. Radio Australia reports that community leaders in North Queensland, just across the strait from New Guinea, fear that China’s plan to construct the facility will jeopardize border security and threaten the commercial fishing sector. There are also concerns that Beijing will attempt to militarize the outpost, seeking to counterbalance the new US-Australian naval base planned for PNG’s Manus Island. (Map: Torres Strait Regional Authority)