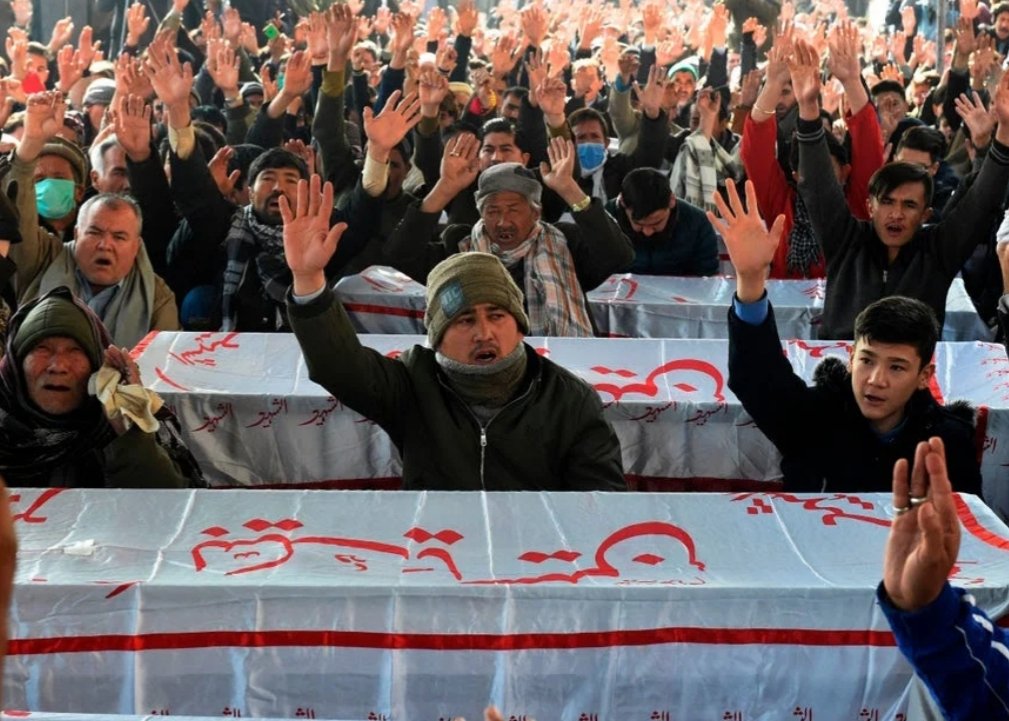
Pro-autonomy protesters killed in Angola
Angolan security forces killed more than 10 people as they protested over living conditions in the diamond-rich town of Cafunfo, in northeastern Lunda Norte province. The demonstration was organized by the Lunda-Tchokwé Protectorate Movement, part of its push for autonomy for a region whose diamond wealth has long lined the pockets of senior ruling party and military figures. The group denied allegations by the security forces that the protesters were armed secessionists who had attempted to break into the police station. (Image via Twitter)