Iran, Hezbollah threaten Argentina: Milei
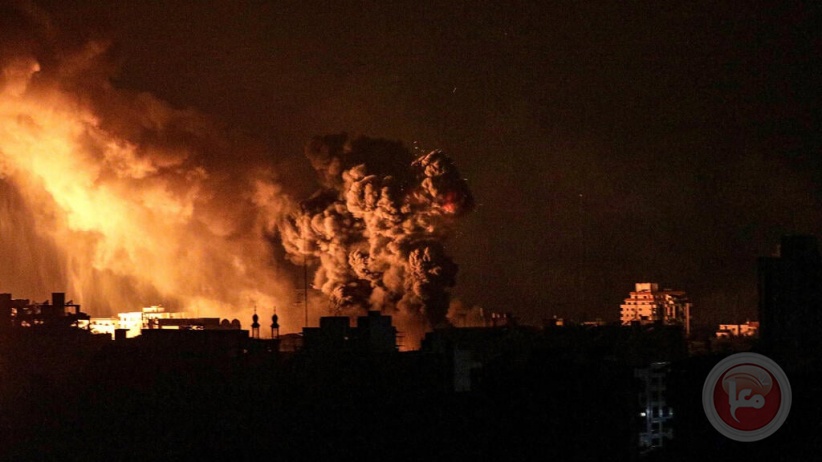
The Argentine government of far-right President Javier Milei announced that it has placed its borders on alert due to potential infiltration of operatives linked to Iran and Hezbollah. There have long been concerns about a Hezbollah presence in the Triborder Region where Argentina, Brazil and Paraguay meet. But Interior Minister Patricia Bullrich in making the announcement this time emphasized a supposed threat from Bolivia. Following years of closer ties, including security cooperation, Bolivia and Iran signed a formal defense pact in July 2023. The deal was said to inlcude an Iranian pledge to provide Bolivia with drones for narcotics enforcement, but the terms were secretive, with both Argentina and the Bolivian opposition demanding clarity on the details. (Photo: Khamenei.ir via Wikimedia Commons)