Syria: rebel forces launch new offensive on Aleppo
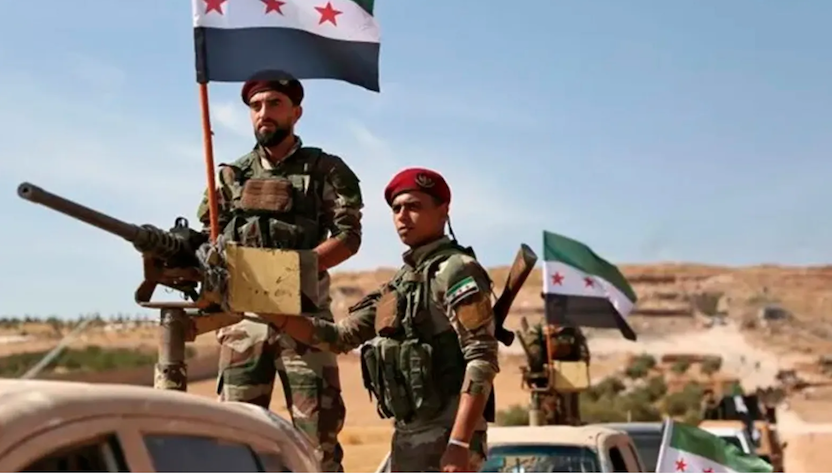
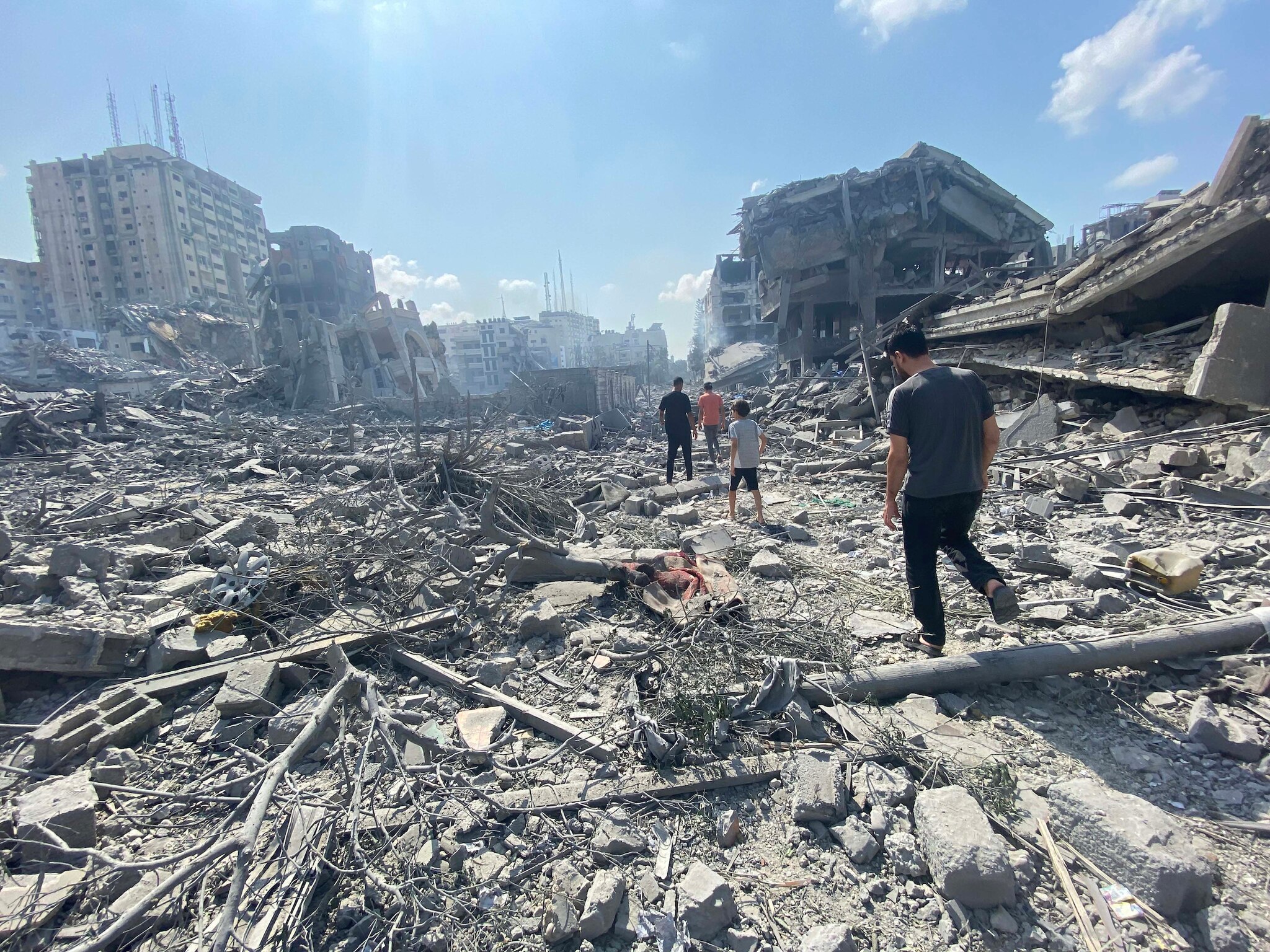
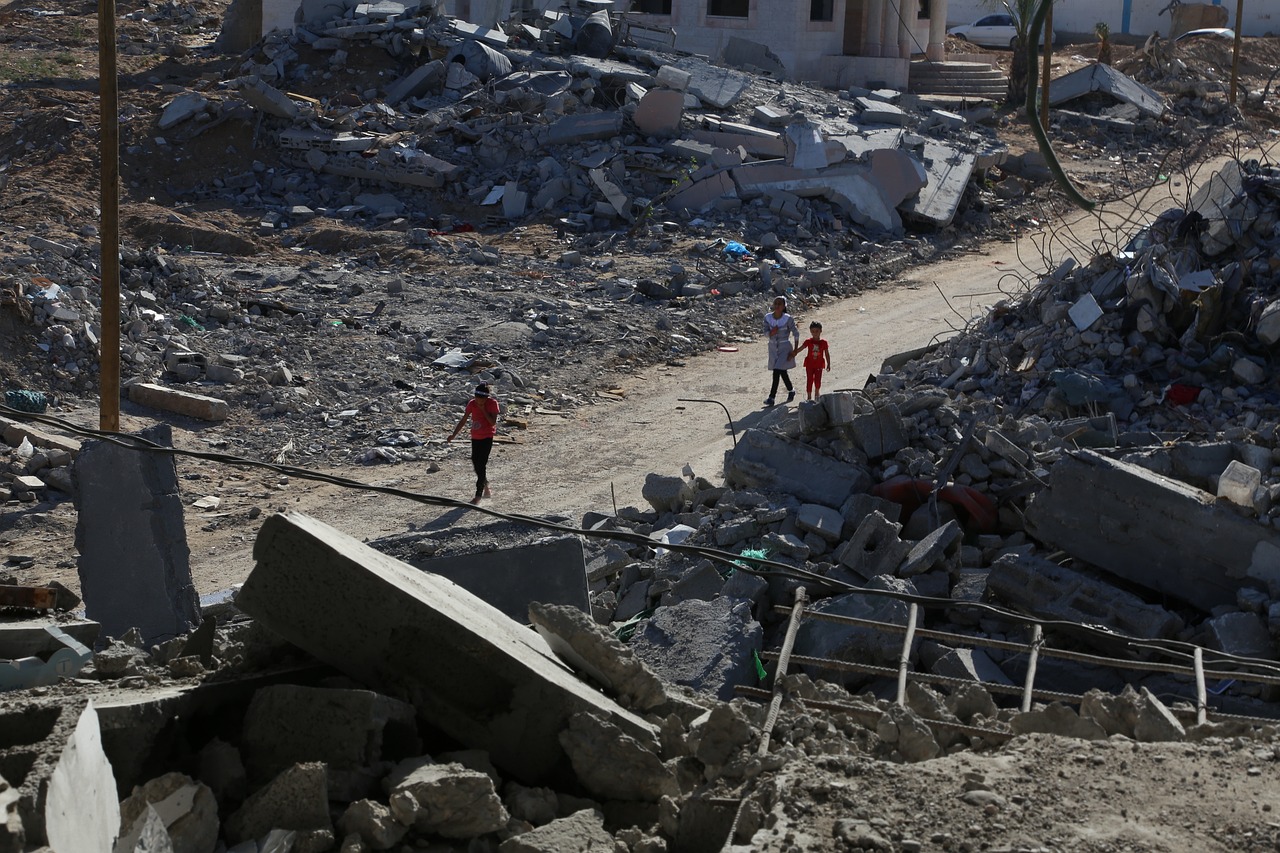
In the most significant escalation in Syria since a 2020 ceasefire instated under emergency conditions during the COVID pandemic, rebel forces in northwestern Idlib province launched a surprise offensive on the country’s most populous city, Aleppo. The rebel advance is said to have penetrated the perimeter of the city, which had been held for years by rebel forces before it was retaken by the regime with the help of Russian air power in 2016. Russia has responded to the new offensive with fresh air-strikes on Idlib, which has been coming under intermittent Russian bombardment for years. At least 225 fatalities are reported in the new fighting, including some 25 civilians killed in Russian air-strikes. (Photo: Syrian Observer)