Sudan war drives continued refugee exodus: UN
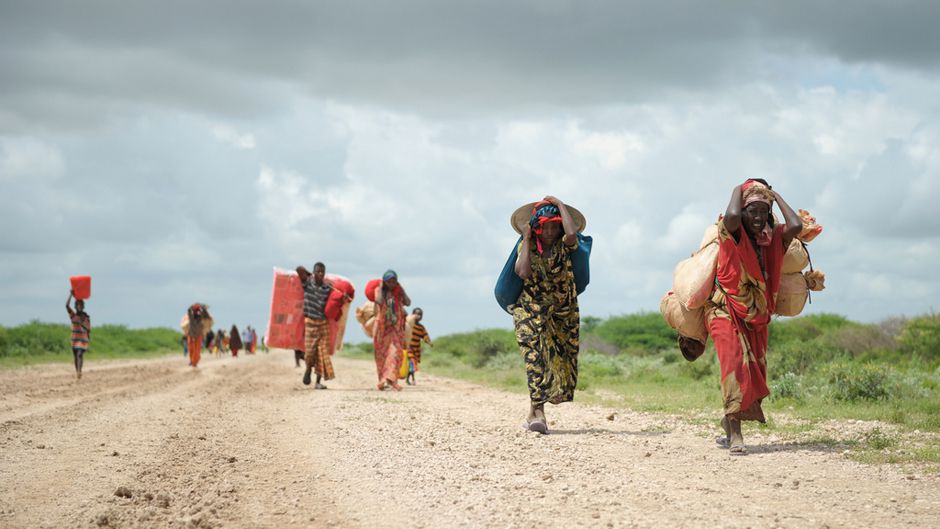
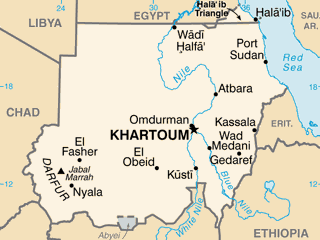
The war in Sudan is driving continued refugee flight, leading to a deepening humanitarian crisis in the greater region, the UN High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) reported. The agency said that more than 3 million people have fled Sudan, seeking safety in neighboring countries, since the war began in April 2023. The refugees are faced with challenges of food shortages and continued rights violations such as killings, sexual violence and looting, as well as natural disasters such as flooding. In October, around 60,000 Sudanese escaping the escalated fighting in Darfur arrived in Chad, which is facing a resource shortage due to its increasing refugee population, now at over 1.1 million. The refugees there face an overwhelmed healthcare system, scarce food, and no education for their children who have already been out of school for two years. (Map: PCL)