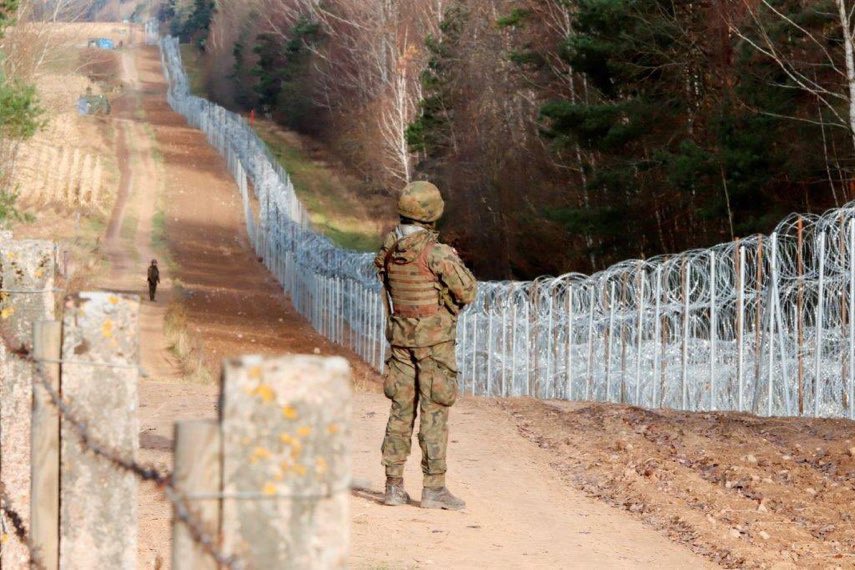
Condemn Poland plan to suspend asylum rights
Over 40 human rights groups have warned Poland’s Prime Minister Donald Tusk against implementing his plan to temporarily suspend the right to claim asylum. Among the groups are Amnesty International, several asylum law organizations, and the Auschwitz-Birkenau Foundation. In an open letter, the organizations stressed that the fundamental right to asylum is binding on Poland under international law, as the country has ratified the Geneva Convention, and under EU law as provided by Article 18 of the Charter of Fundamental Rights. Tusk justified his move as necessary in light of Belarus’ mass transfers of migrants across the border, which he called an act of “hybrid warfare” to threaten Polish national security. (Photo: Visegrad24)