IACHR hearings on state obligations in climate crisis
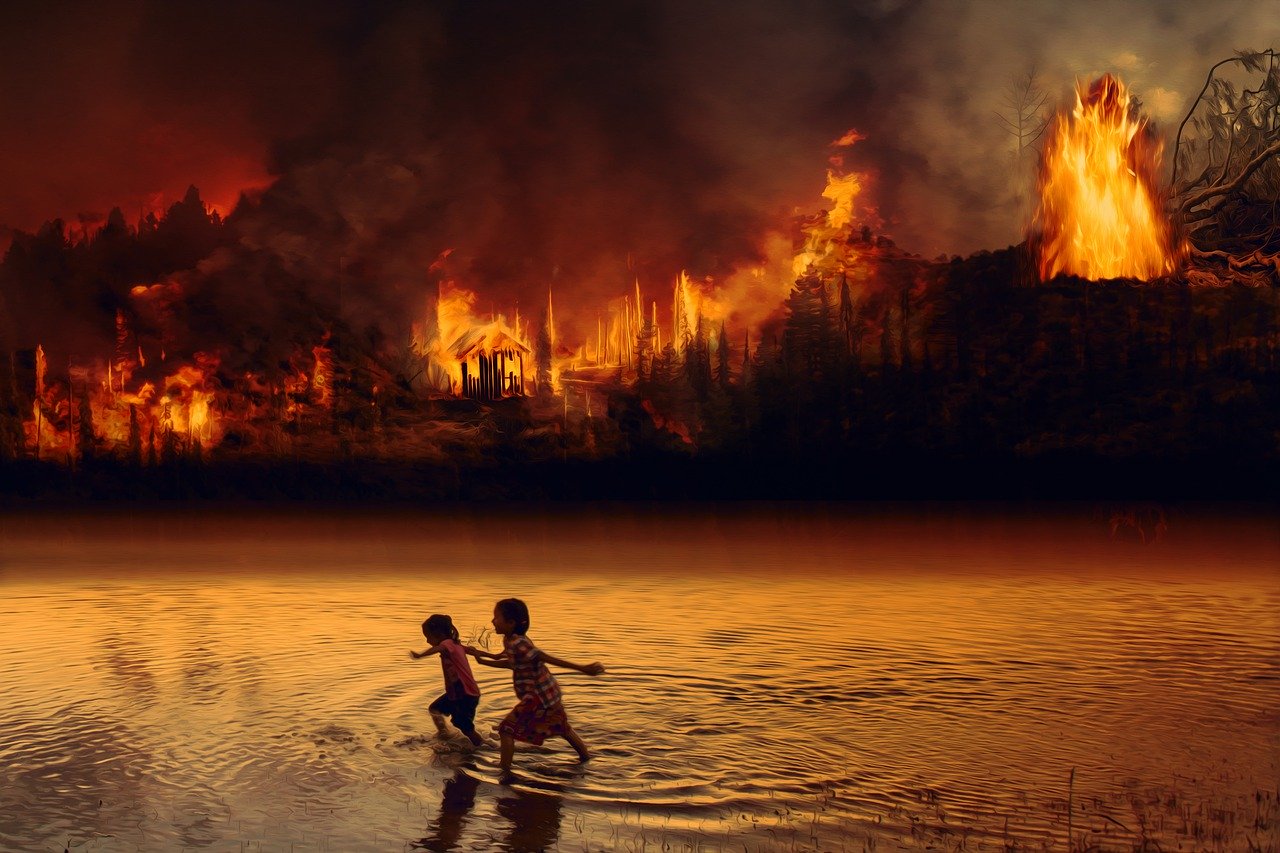
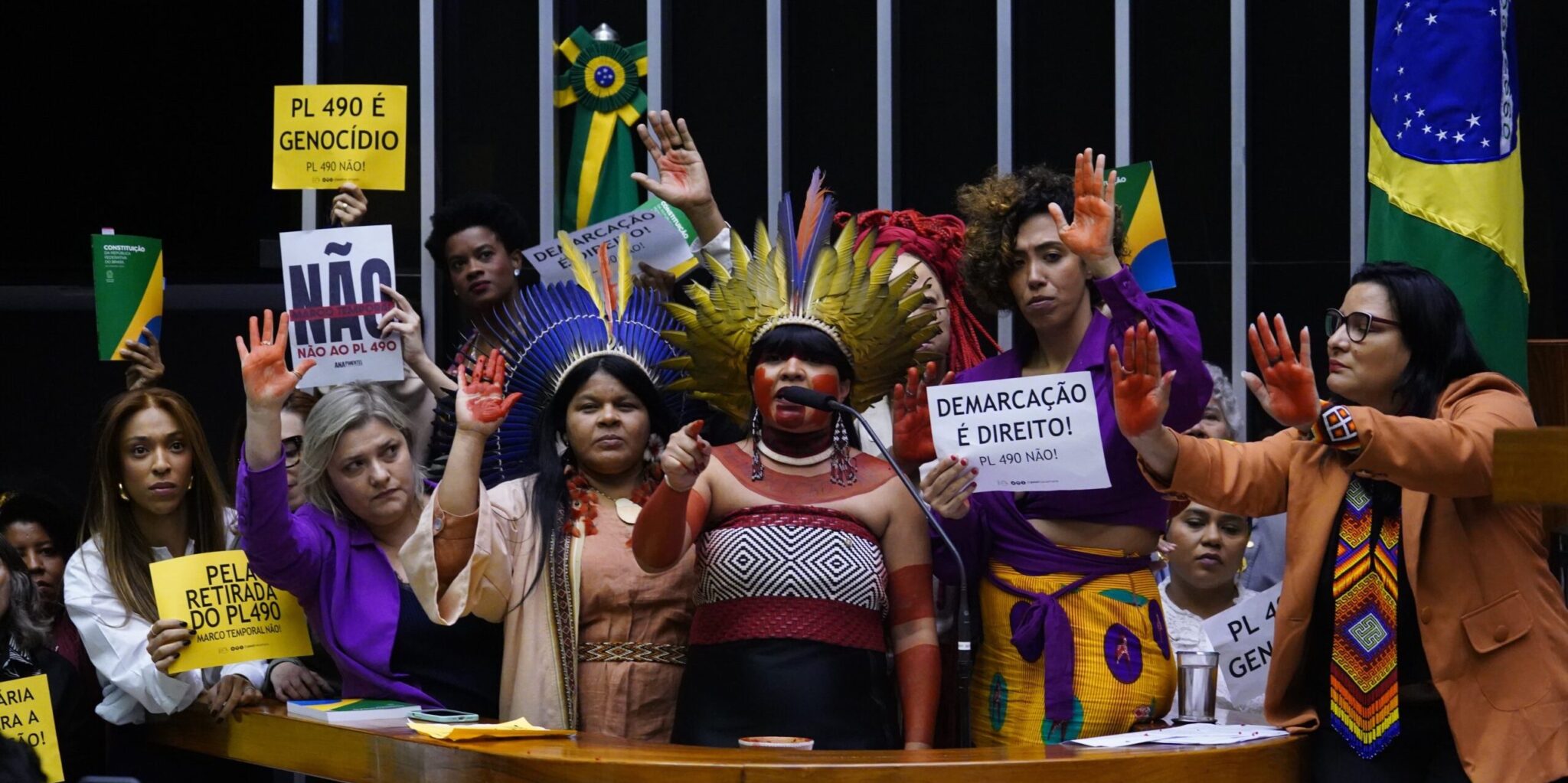
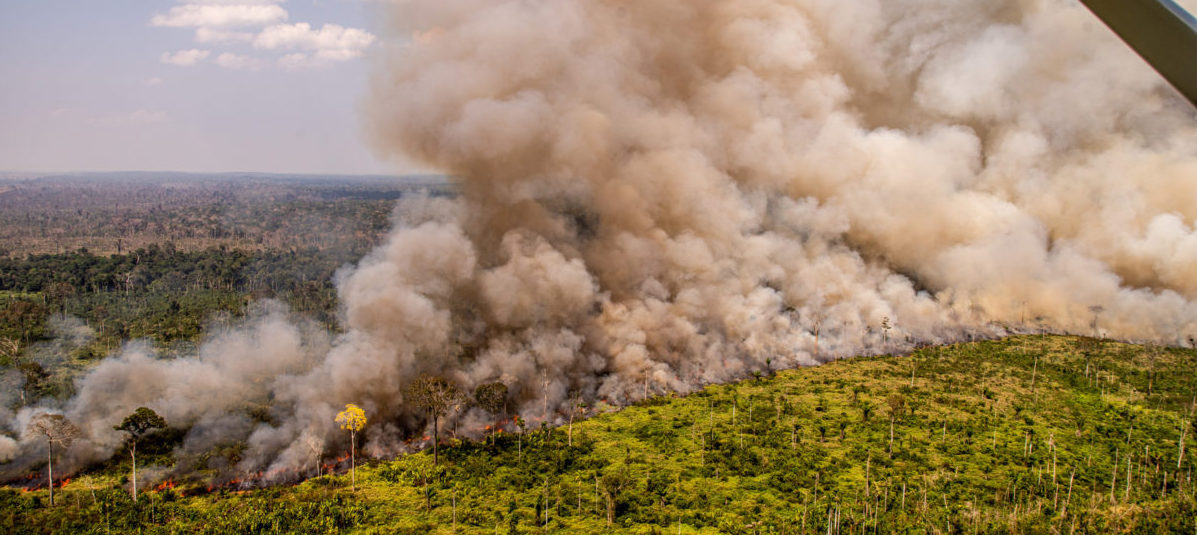
The Inter-American Court of Human Rights (IACHR) began its first day of public hearings in Manaus, Brazil, to address the obligations of states in light of the climate crisis, based on the principles of the American Convention on Human Rights. The hearings, marked by discussion on mitigating the impacts of social imbalances and the need to protect the most vulnerable, follow a January request by Chile and Colombia for an Advisory Opinion on the Climate Emergency and Human Rights. The first hearings took place in Barbados at the end of April. In their request, Chile and Colombia emphasized the devastating consequences of the climate emergency in their countries, citing examples such as droughts, floods, landslides and fires. (Photo: pixundfertig/Pixabay via Jurist)