Deadly strikes on hospitals: the new norm?
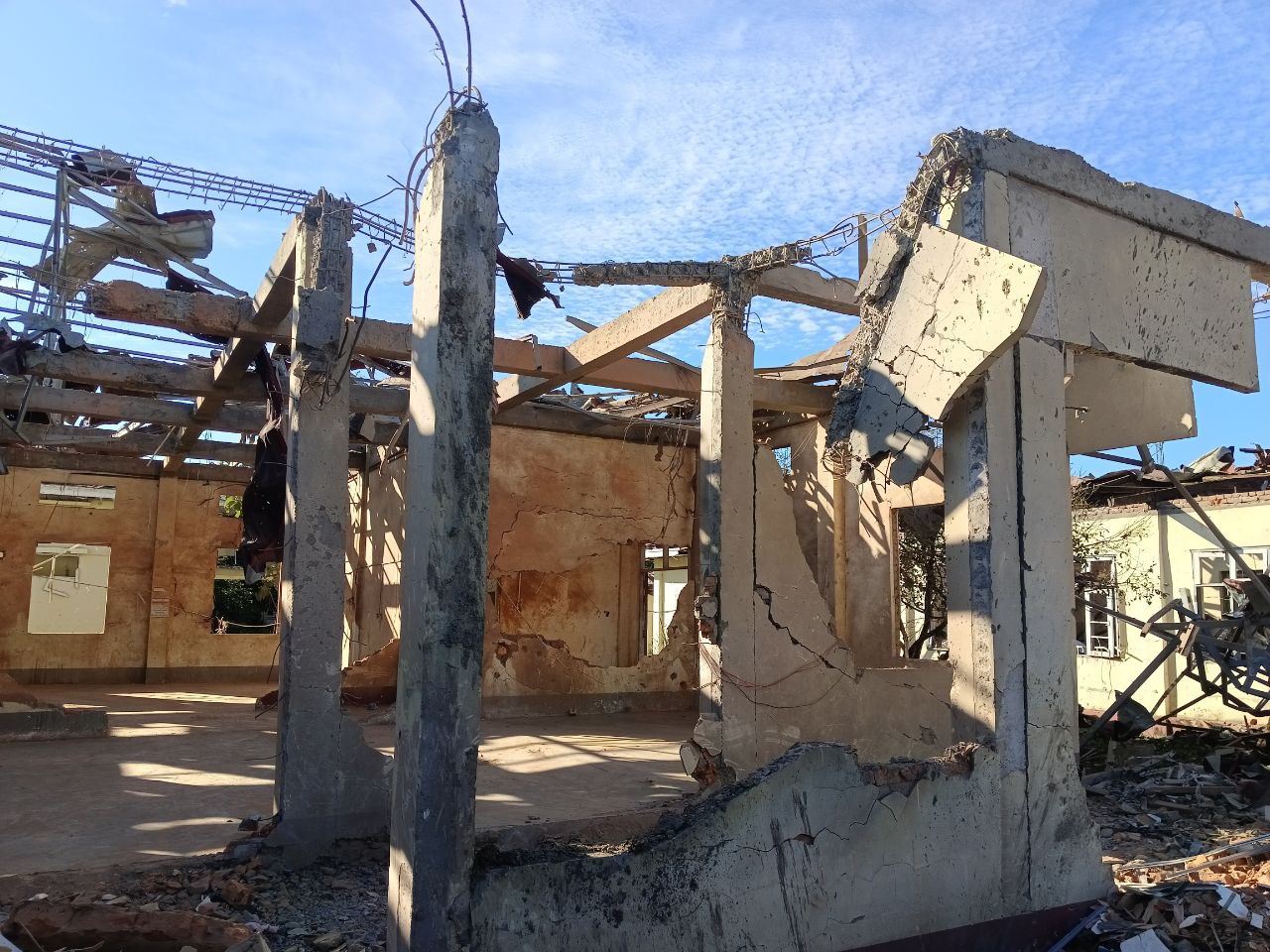
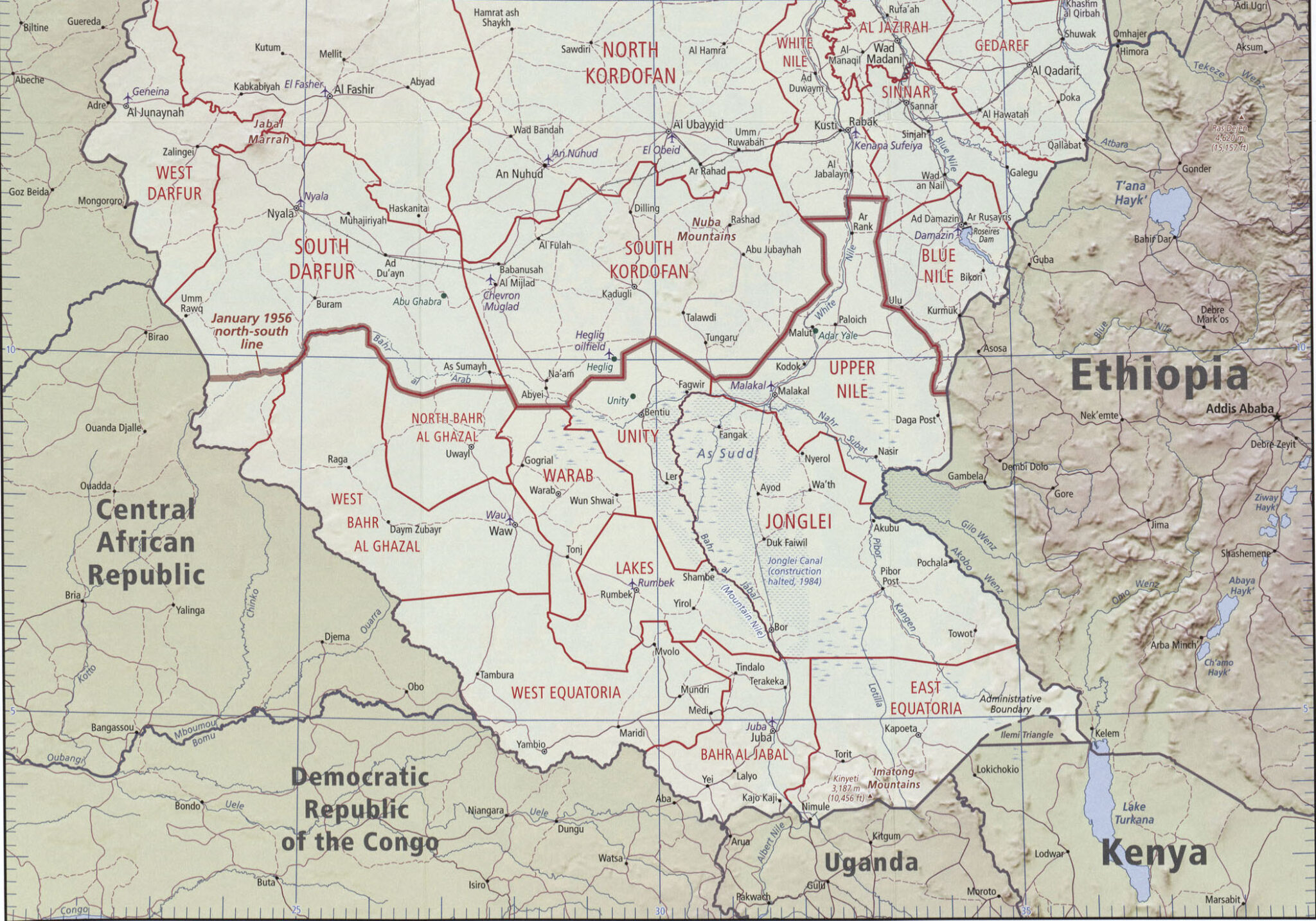
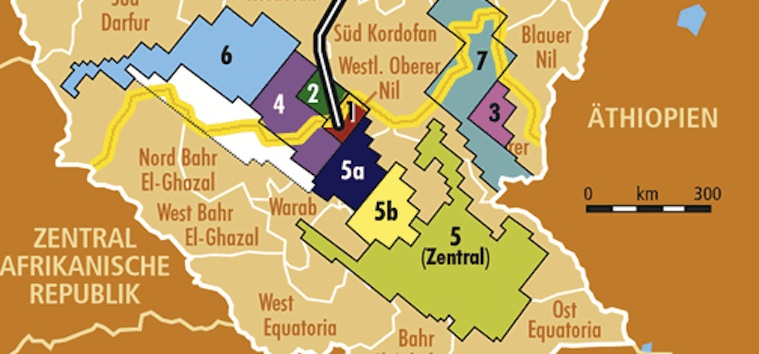
On World Humanitarian Day in August, World Health Organization director-general Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus released a statement calling attention to intensifying attacks on healthcare workers and facilities, which constitute war crimes under international humanitarian law. “We must stop this becoming the norm,” he wrote. The events of the past weeks suggest such attacks are now already the norm. In Sudan, the WHO reported that over 100 people, including 63 children, were killed when drone strikes attributed to the Rapid Support Forces hit a kindergarten and nearby hospital in South Kordofan. In Burma’s Rakhine state, a military airstrike destroyed the Mrauk-U general hospital, killing at least 31 people and wounding dozens more. It was the 67th attack on a healthcare facility in Burma this year, according to the WHO. Attacks on healthcare facilities killed a record 3,600 people in 2024, mainly in Gaza, Ukraine, Lebanon, Burma and Sudan. This year is on course to surpass that toll. In Gaza alone, at least 917 people were killed by Israeli attacks on healthcare facilities between Oct. 7. 2023 and June of this year. (Photo: Myanmar Now)